Slide 1 - Properties of Angles
This title slide introduces "Properties of Angles" for Class 7 CBSE Mathematics. The subtitle highlights exploring key concepts in geometry.
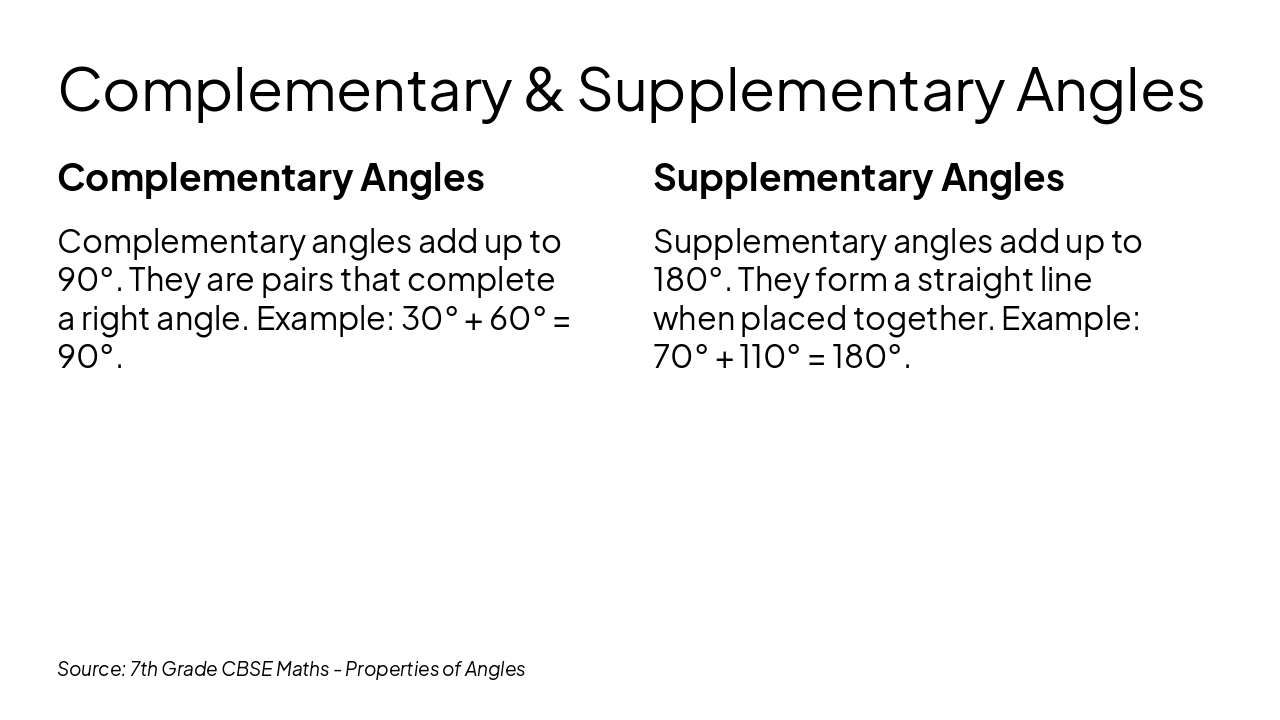
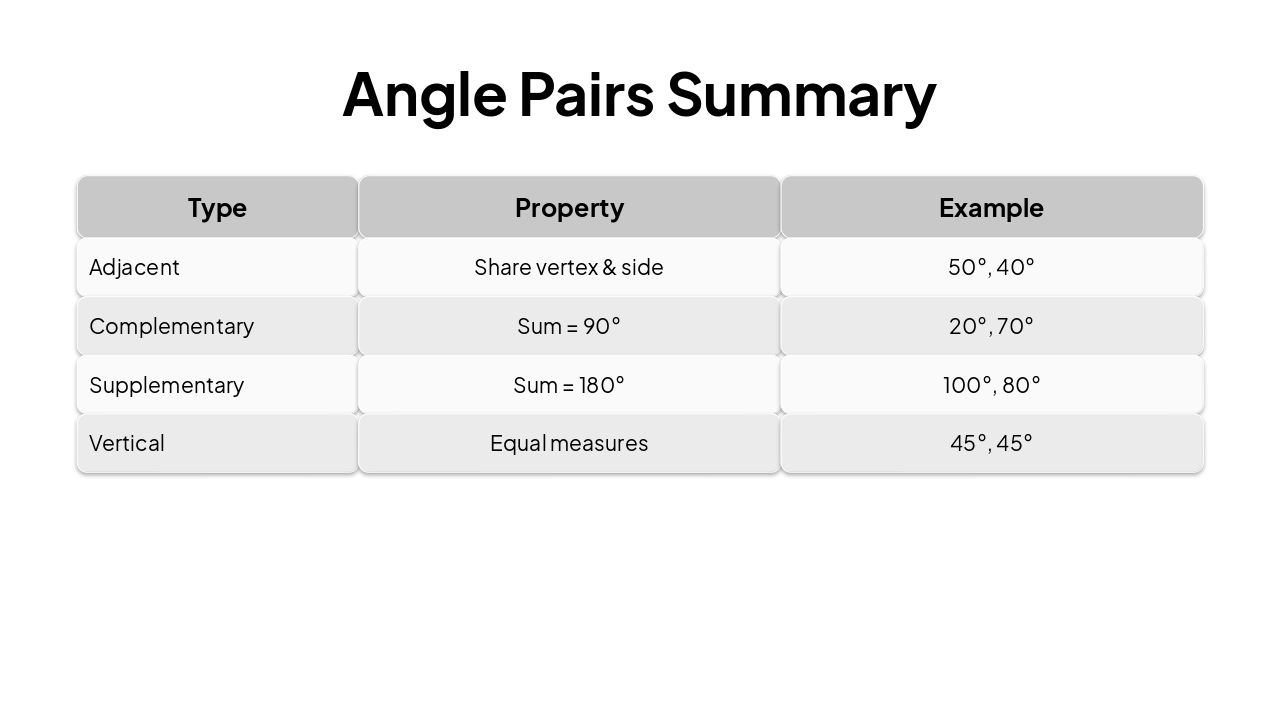
Properties of Angles
Class 7 CBSE Mathematics
Exploring Key Concepts in Geometry
Source: Class 7 CBSE Mathematics