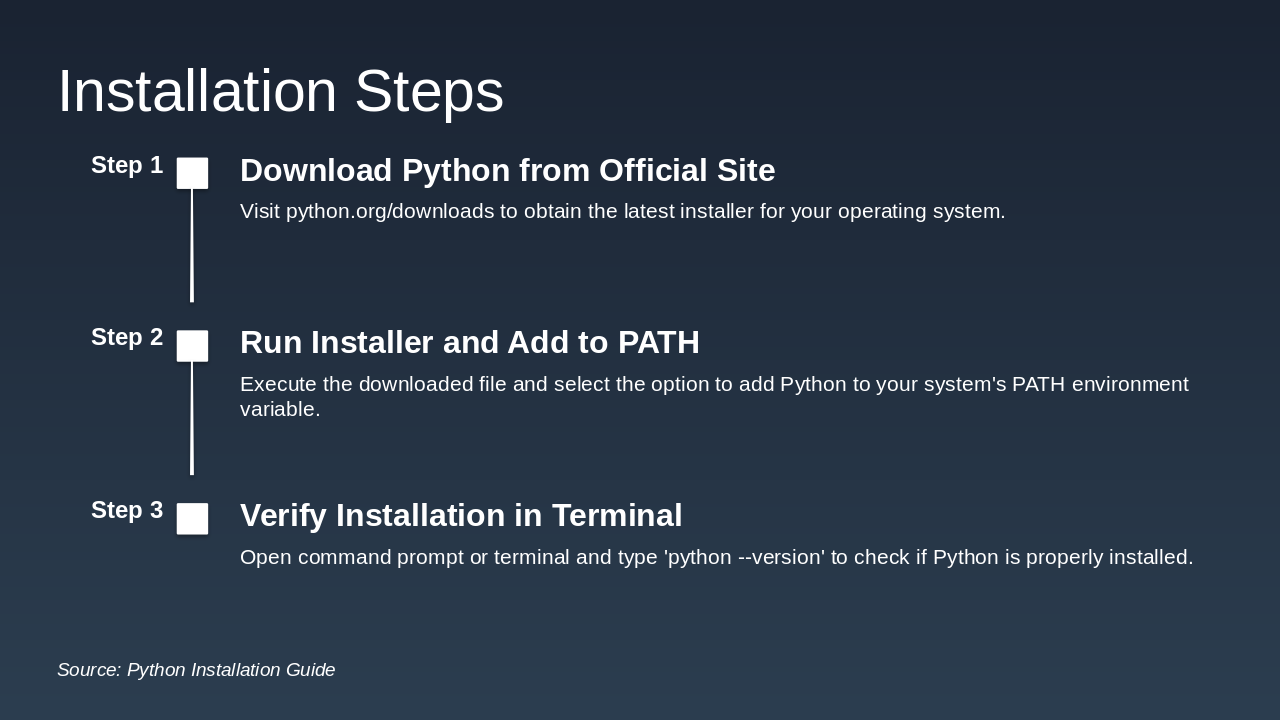
Slide 1 - Python Installation Guide
This title slide introduces a comprehensive Python Installation Guide. It covers key topics including installation procedures, environment setup, and core concepts.
Python Installation Guide
Installation, Environment Setup, and Core Concepts
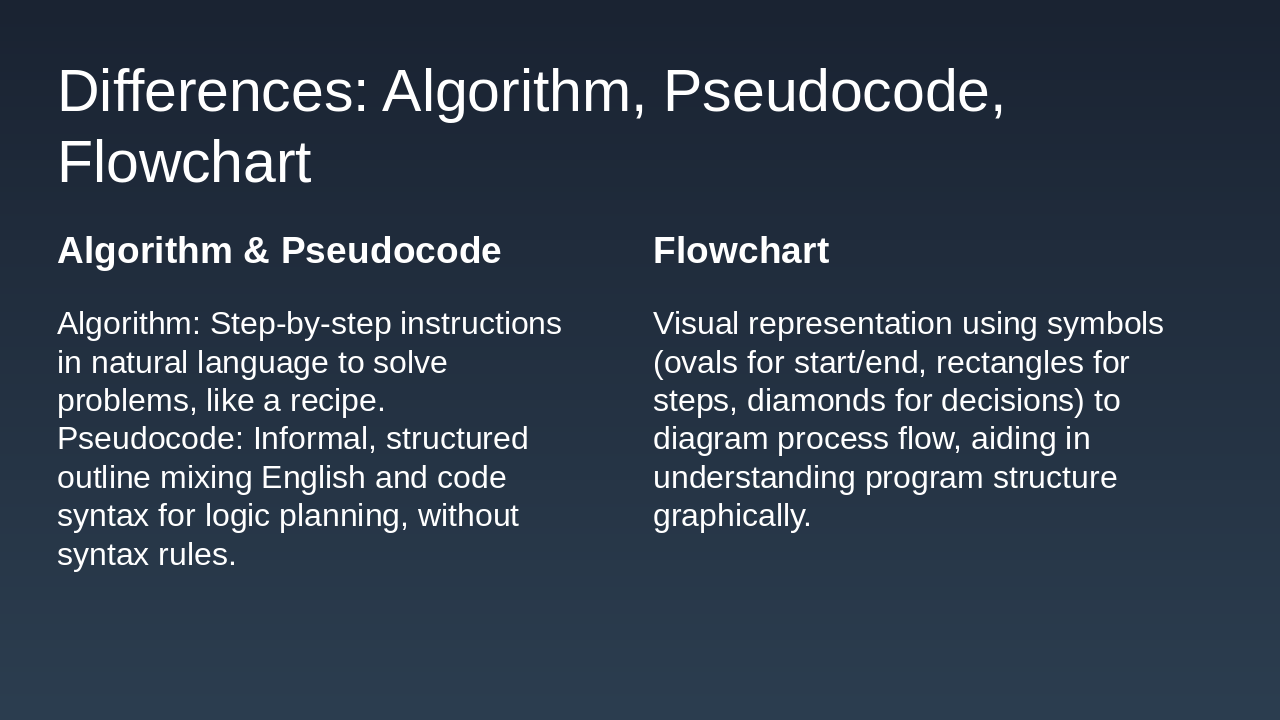
--- Speaker Notes: Introduction to installing Python, setting environment variables, and explaining key concepts like algorithms, pseudocode, and flowcharts.