Slide 1 - Fundamentals of Energy and Conservation
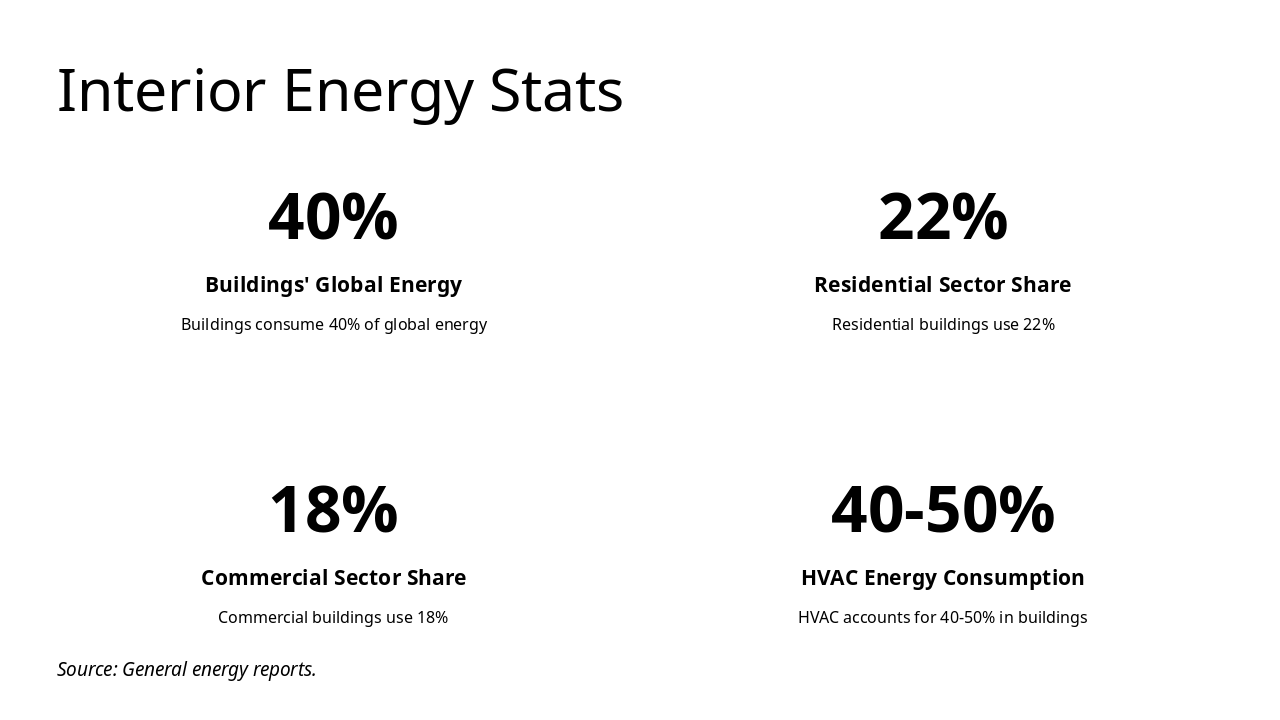
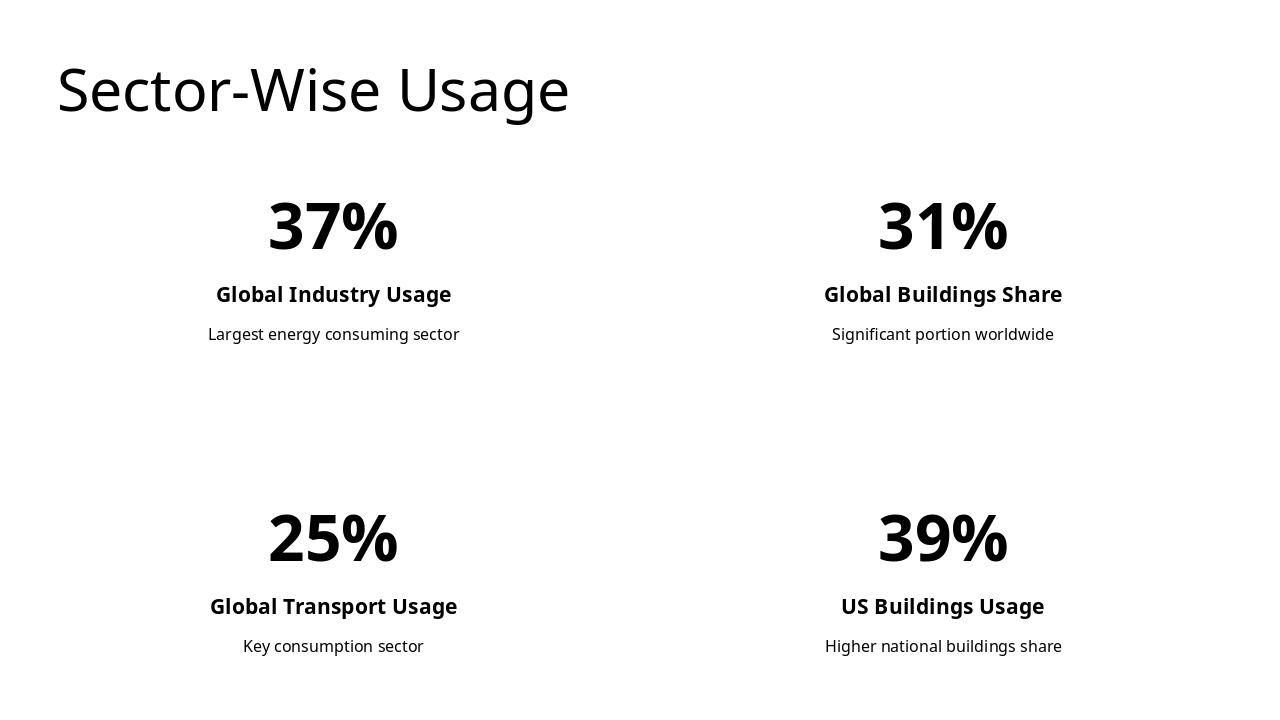
This title slide is named "Fundamentals of Energy and Conservation." Its subtitle outlines explorations of energy basics, interiors consumption, conservation strategies, and global scenarios for sustainable design.
Fundamentals of Energy and Conservation
Exploring energy basics, consumption in interiors, conservation strategies, and global scenarios for sustainable design.