Slide 1 - Principle, Theory, and Types of Titration
Principle, Theory, and Types of Titration
Fundamentals of titration in analytical chemistry and role of indicators
Generated from prompt:
Principal and Theory of titration and types of titration and chemistry about indicators
Explore titration's core principles, theory based on stoichiometric reactions, types (acid-base, redox, etc.), equivalence points, and indicator chemistry for precise chemical analysis. (148 character
Principle, Theory, and Types of Titration
Fundamentals of titration in analytical chemistry and role of indicators

Fundamentals and principles of titration processes.
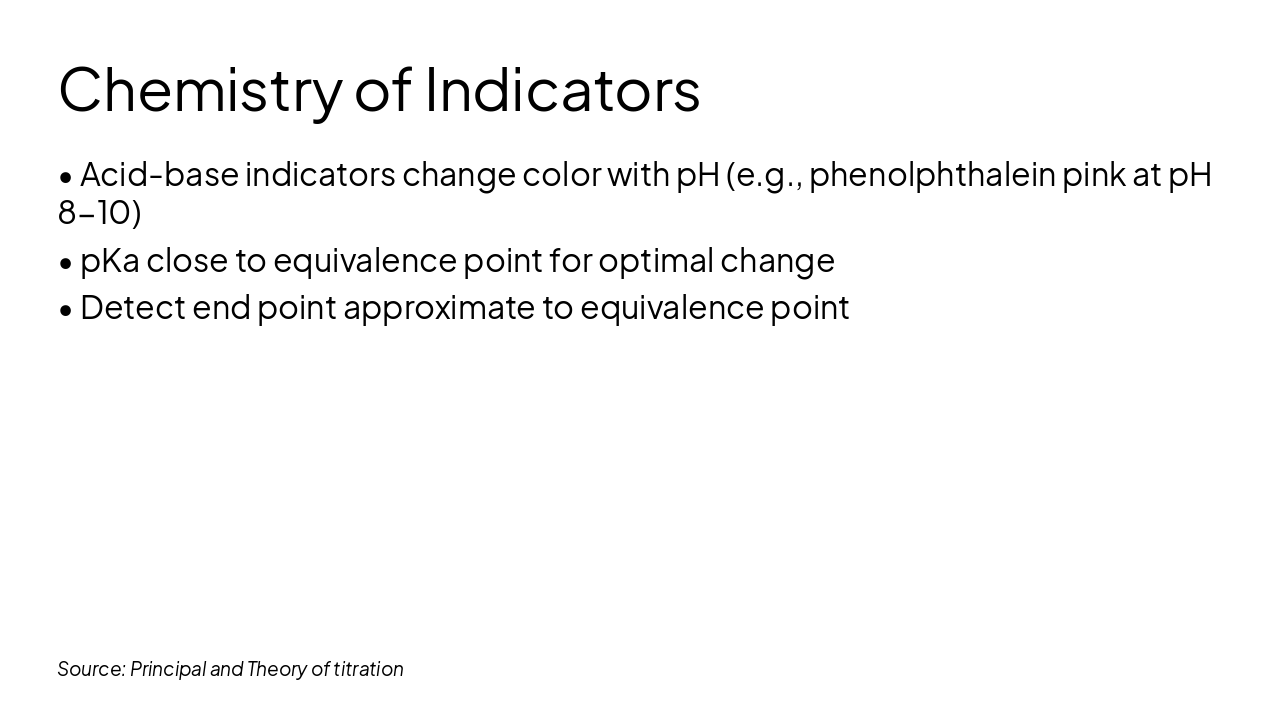
Chemical theory underlying titration reactions and equilibria.
Classification and examples of different titration methods.
Role and selection of chemical indicators in titrations.
Practical applications and final summary of titration.

01
Determination of concentration through stoichiometric reaction with known solution



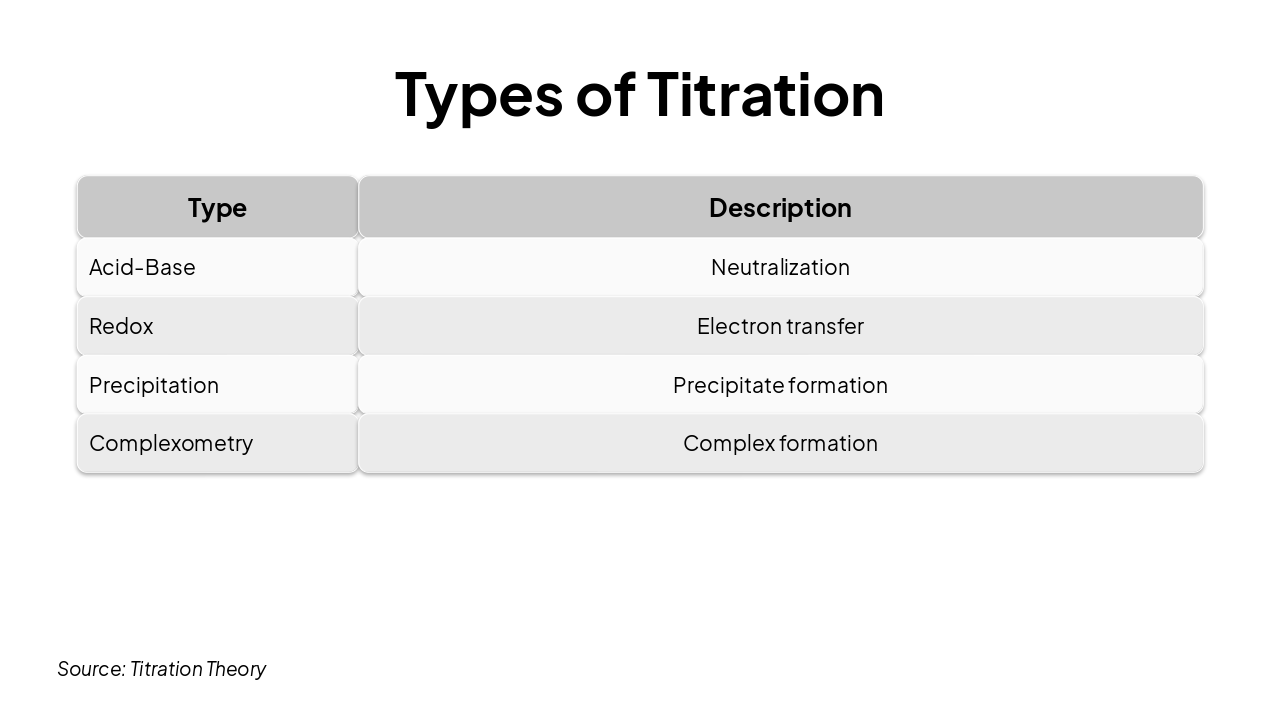
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Acid-Base | Neutralization |
| Redox | Electron transfer |
| Precipitation | Precipitate formation |
| Complexometry | Complex formation |

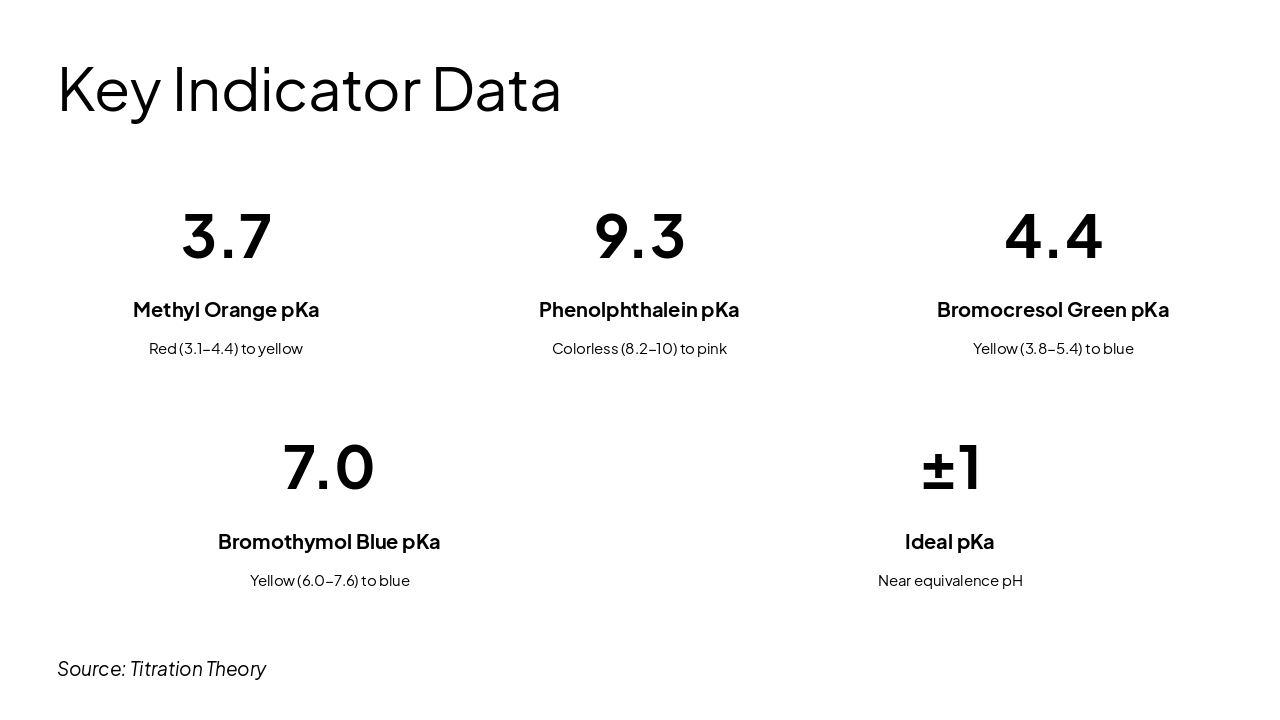
Red (3.1-4.4) to yellow
Colorless (8.2-10) to pink
Yellow (3.8-5.4) to blue
Yellow (6.0-7.6) to blue
Near equivalence pH
Precise titration: key in chemical analysis.
Thanks! Contact: help@karaf.ai

Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.