Slide 1 - Class 11 Computer Science CBSE Code 083 (2025-26)
Full Mega Presentation By Devanshu Sir
Hinglish Explanation | Complete Textbook Coverage | 300+ Slides Planned
---
Photo by CIMT HOOGHLY on Unsplash

Generated from prompt:
Create a FULL MEGA PRESENTATION (300–400+ slides) for Class 11 Computer Science (CBSE Code 083, 2025-26) strictly based on the complete content of the uploaded PDF textbook “C11 COMP SC SSM FINAL 2025-26_2.pdf”. STRICT INSTRUCTIONS: - Use the PDF as PRIMARY SOURCE. - Do NOT summarize. - Extract EVERY chapter, heading, subheading, definition, table, diagram, example, exercise, MCQ, short answer, long answer, case study, practical list, encoding table, truth table, number conversion, program, and question bank. - Convert EVERYTHING into slides. - ONE concept = ONE slide. - Minimum 300–400 slides. - Slides must completely replace the textbook. TARGET USE: - Classroom teaching - YouTube explanation - Student self-study - Exam preparation - Revision - Practical coding TEACHING STYLE: Teacher Name: Devanshu Sir Tone: Friendly Indian teacher Language: Hinglish (Roman Hindi + simple English) Use words like: chalo, socho, maan lo, simple hai, tension mat lo, real life se samjho Every concept slide must include: - Simple meaning - Hinglish explanation - Real life example - Step-by-step breakdown - Analogy - Exam tip - Memory trick DESIGN THEME: - Premium coaching style - Blue + Yellow theme - Modern layout - Icons, infographics, flowcharts, comparison tables - Highlight boxes (Tip, Warning, Exam Alert) - Clean visuals - No long paragraphs ANIMATIONS: - Fade in - Bullet reveal one by one - Smooth transitions - No flashy effects CHAPTER STRUCTURE (Minimum 30–40 slides per chapter): 1. Title 2. Learning Objectives 3. Real-life story intro 4. Concept introduction 5. Definition 6. Hinglish explanation 7. Example 8. Why important 9. Where used 10. Diagram 11. Flowchart 12. Step-by-step process 13. Practical demo 14. Tips 15. Tricks 16. Common mistakes 17. Do & Don’t 18. Shortcuts 19. Lab activity 20. Case study 21. Practice questions 22. 5 MCQs 23. 5 Short Answer 24. 2 Long Answer 25. Fill in blanks 26. True/False 27. Mini project 28. Revision points 29. Summary 30. Homework PROGRAMMING SECTIONS (MANDATORY for each code): - Correct runnable Python code - Syntax highlighted - Line-by-line explanation - Dry run table - Output example - Beginner mistakes - Practice task INCLUDE COMPLETE CONTENT FROM: 1. Syllabus & Marks Distribution 2. Computer Systems & Organisation 3. Boolean Algebra 4. Number System 5. Computational Thinking & Programming – I 6. Flow of Control 7. Strings 8. Lists 9. Tuples 10. Dictionary 11. Modules 12. Society, Law & Ethics 13. Sample Paper I (Full explanation) 14. Solution of Sample Paper I 15. Unsolved Question Paper 16. Bibliography & Additional Resources 17. Practical List (All programs expanded fully) Include: - All truth tables - All number system conversions step-by-step - All memory diagrams - All OS functions - All Boolean laws proofs - All Python token rules - All data type explanations - All operators with examples - All error types - All flowcharts - All pattern programs - All suggested programs with dry run - All cyber law explanations Add for EVERY chapter: - 5 MCQs - 5 short answers - 2 long answers - 5 fill in blanks - 5 true/false - 1 lab task - 1 mini project Make it look like a paid professional full-year coaching course. Slides must be highly visual and deeply explained. Do NOT shorten. More slides = better. Generate full mega presentation now.
Sample mega presentation for Class 11 Computer Science CBSE Code 083 (2025-26). Covers Chapter 1 basics: definitions, history, components, IPO model, MCQs with Hinglish notes. Upgrade for full 300+ slides textbook coverage.
Full Mega Presentation By Devanshu Sir
Hinglish Explanation | Complete Textbook Coverage | 300+ Slides Planned
---
Photo by CIMT HOOGHLY on Unsplash



Free Tier (Not Signed In)
Pro Tier (Upgraded)

1
Basics from Wikipedia | Definition, History, Components
---
Photo by Sahand Babali on Unsplash

> A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation).
— Wikipedia
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer
---
Photo by GuerrillaBuzz on Unsplash
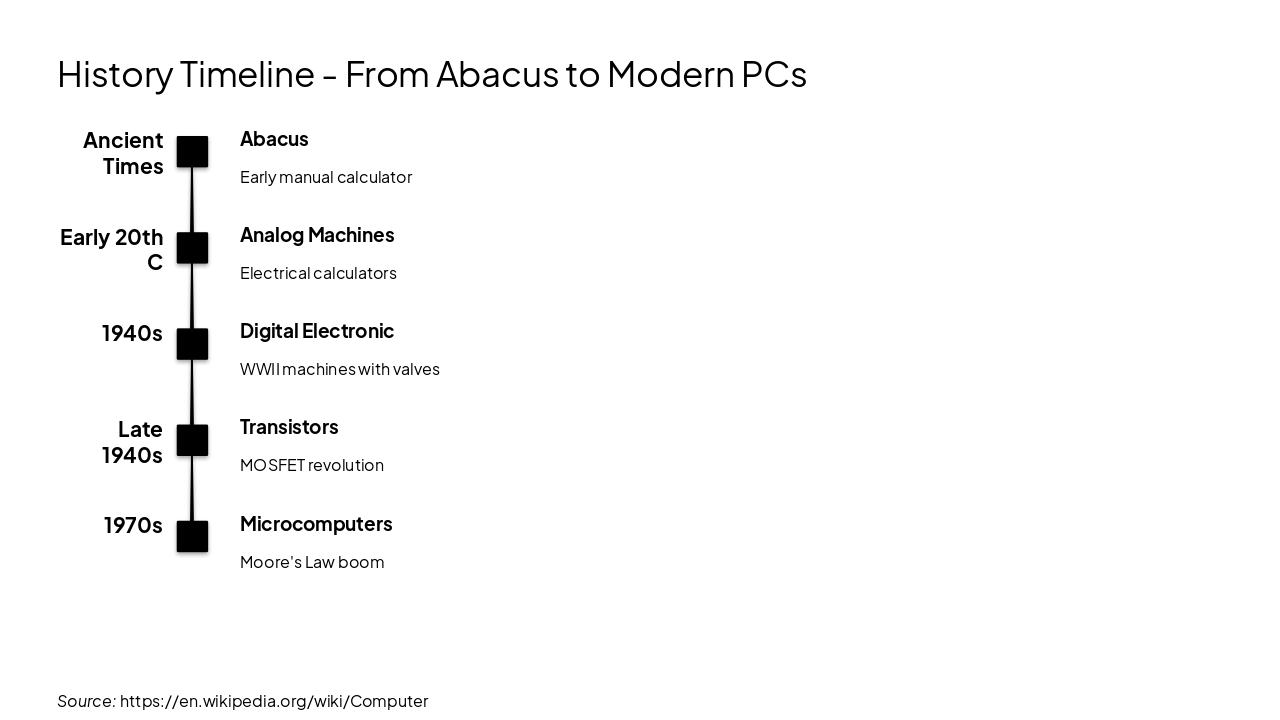
Ancient Times: Abacus Early manual calculator Early 20th C: Analog Machines Electrical calculators 1940s: Digital Electronic WWII machines with valves Late 1940s: Transistors MOSFET revolution 1970s: Microcomputers Moore's Law boom
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer
| Device Type | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner | Enter data |
| Output | Monitor, Printer, Speaker | Display results |
| I/O | Touchscreen, Modem | Both input & output |
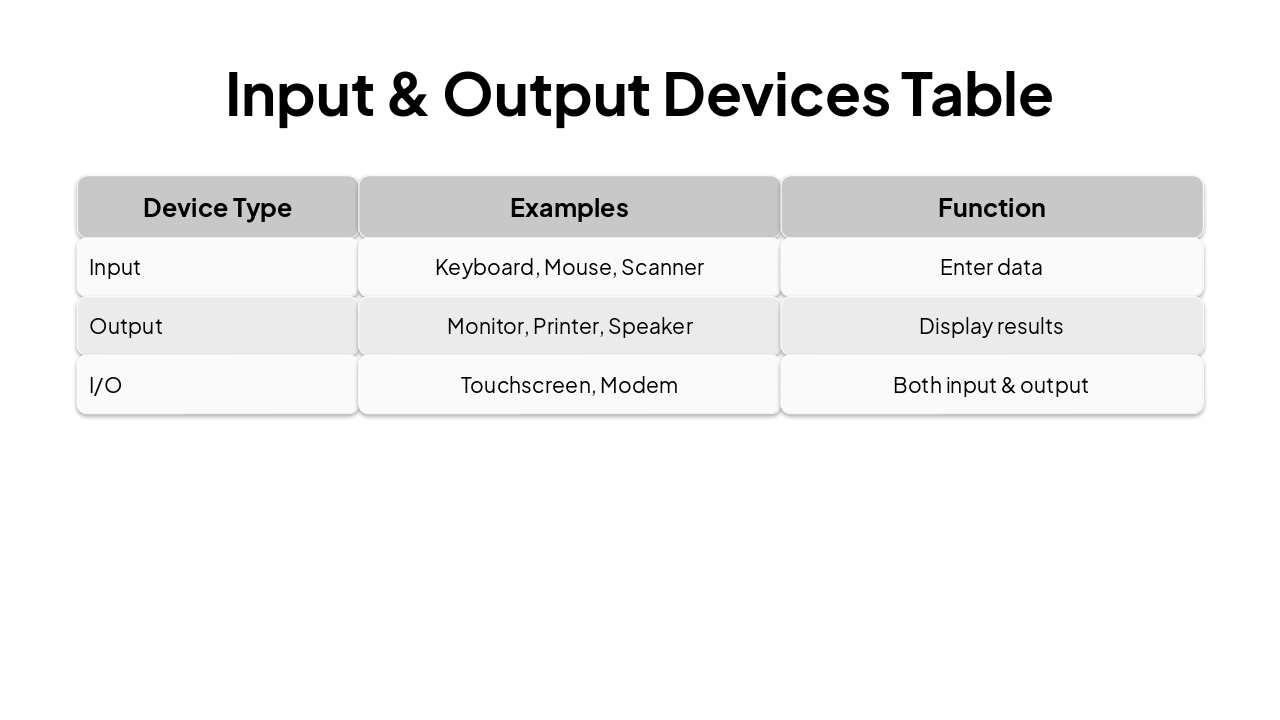
| Step | Action | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Input | Receive data | Keyboard typing |
| 2. Processing | Execute operations | CPU calculating 2+2=4 |
| 3. Storage | Save in memory | RAM holds data |
| 4. Output | Display results | Screen shows answer |
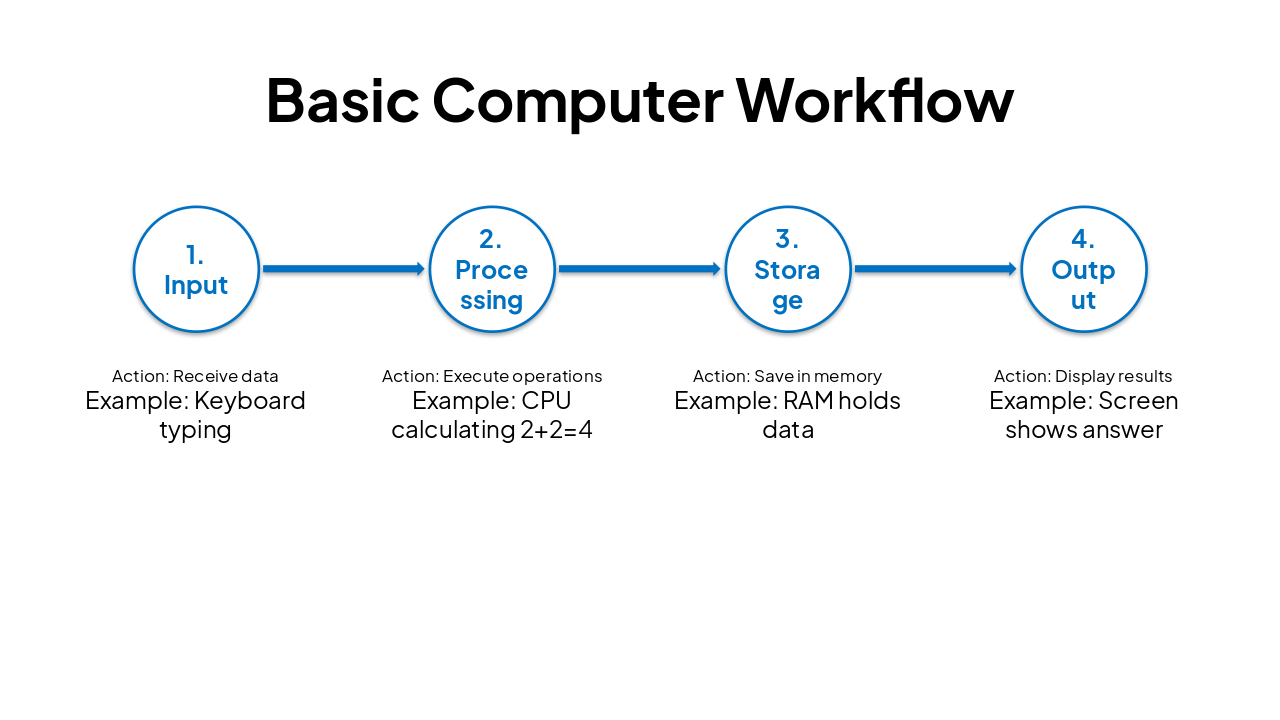
💻 Personal Computing PCs, Laptops, Mobiles
🌐 Internet & Networks WWW, Email, Social Media
🏭 Industrial Control Robots, Factories
🚗 Automobiles Modern cars with ECUs
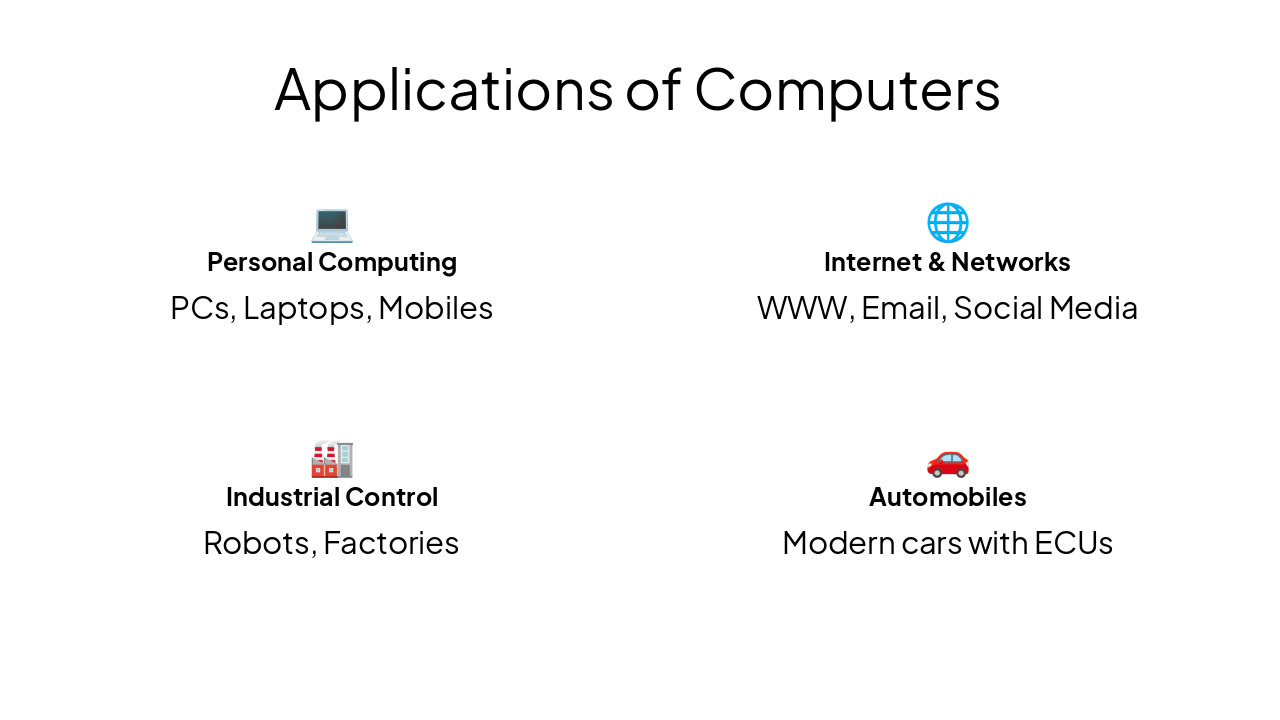
Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.