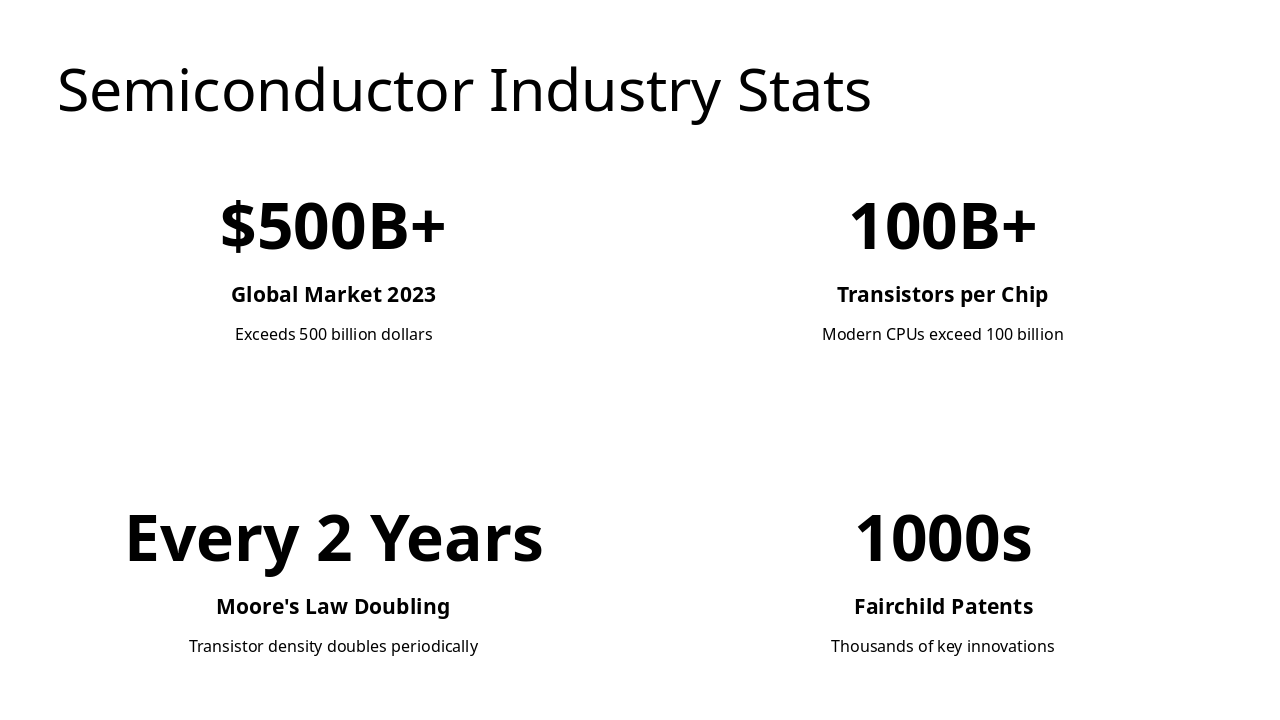
This slide, titled "Innovation Quote," features a statement praising the Traitorous Eight—engineers who left Shockley to found Fairchild Semiconductor—for sparking Silicon Valley's semiconductor revolution and shaping modern technology. The quote is by Jay Last, a co-founder of Fairchild and Silicon Valley pioneer.
Innovation Quote
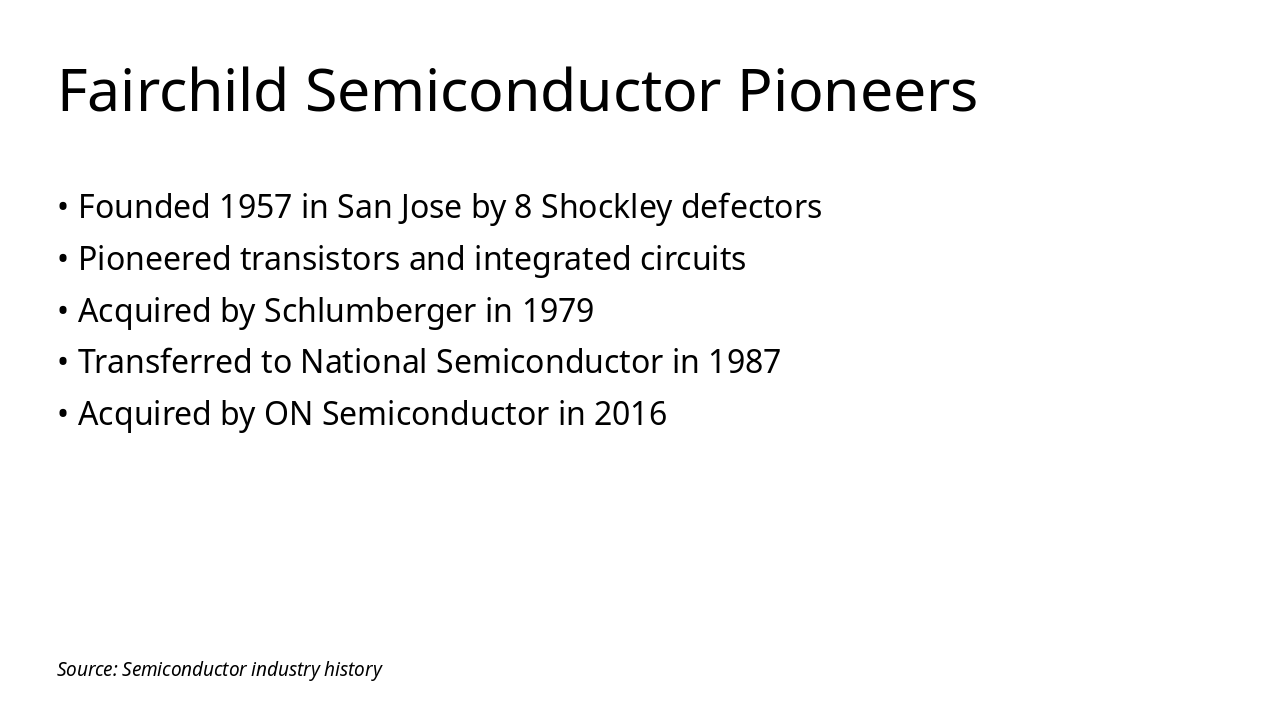
> The Traitorous Eight—visionary engineers who left Shockley to found Fairchild Semiconductor—changed the world, igniting Silicon Valley's semiconductor revolution and shaping modern technology.
— Jay Last, Co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Silicon Valley Pioneer
Source: Fairchild Semiconductor History
Speaker Notes
On Fairchild founders who revolutionized Silicon Valley.