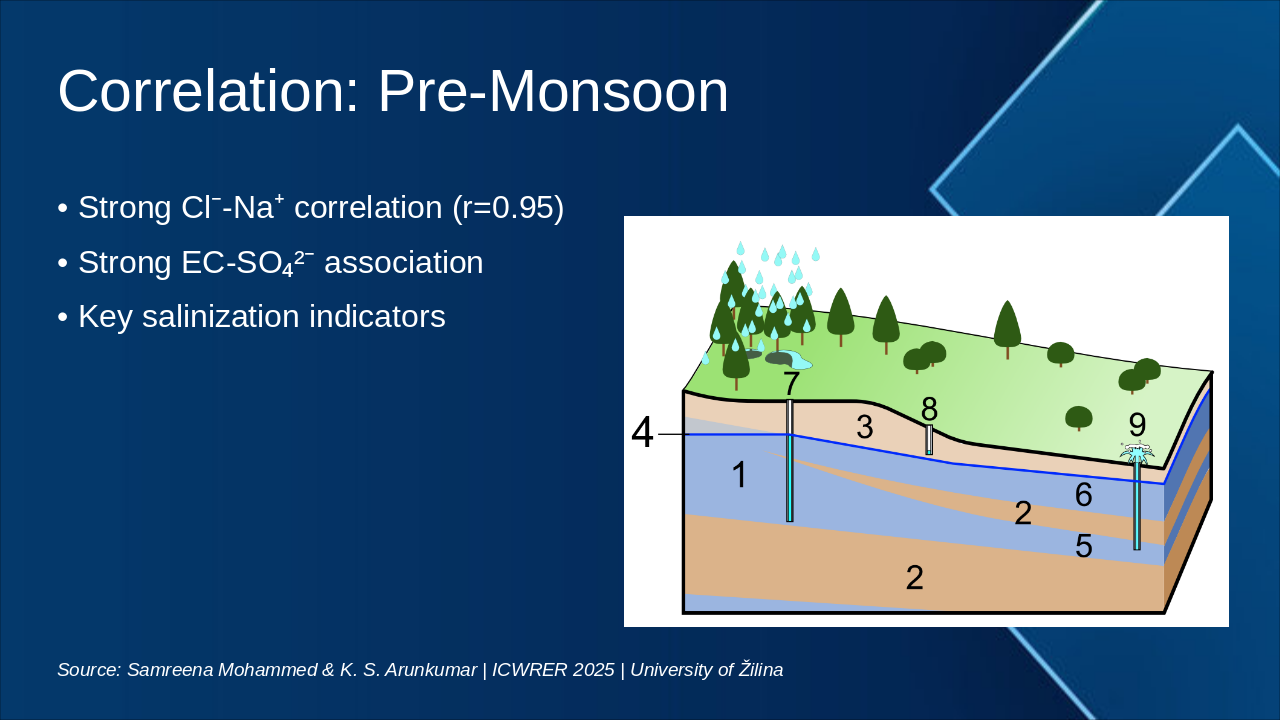
Slide 1 - Title Slide
This title slide features the presentation titled "Assessing Groundwater Resources in Central Kerala, India," using a multivariate statistical approach. It credits authors Samreena Mohammed and K. S. Arunkumar, for the ICWRER 2025 conference at the University of Žilina, with logo placeholders.
Assessing Groundwater Resources in Central Kerala, India
A Multivariate Statistical Approach Samreena Mohammed & K. S. Arunkumar ICWRER 2025 | University of Žilina [Conference logo placeholders]},