Slide 1 - Member 6 – Air Distribution System Design
This title slide introduces Member 6 on Air Distribution System Design, highlighting key topics like Duct Design, Airflow Measurement, Fans/Blowers, and Diffusers and Grilles. It includes a subtitle crediting [Your Name] as presenter for the course [Insert course name].
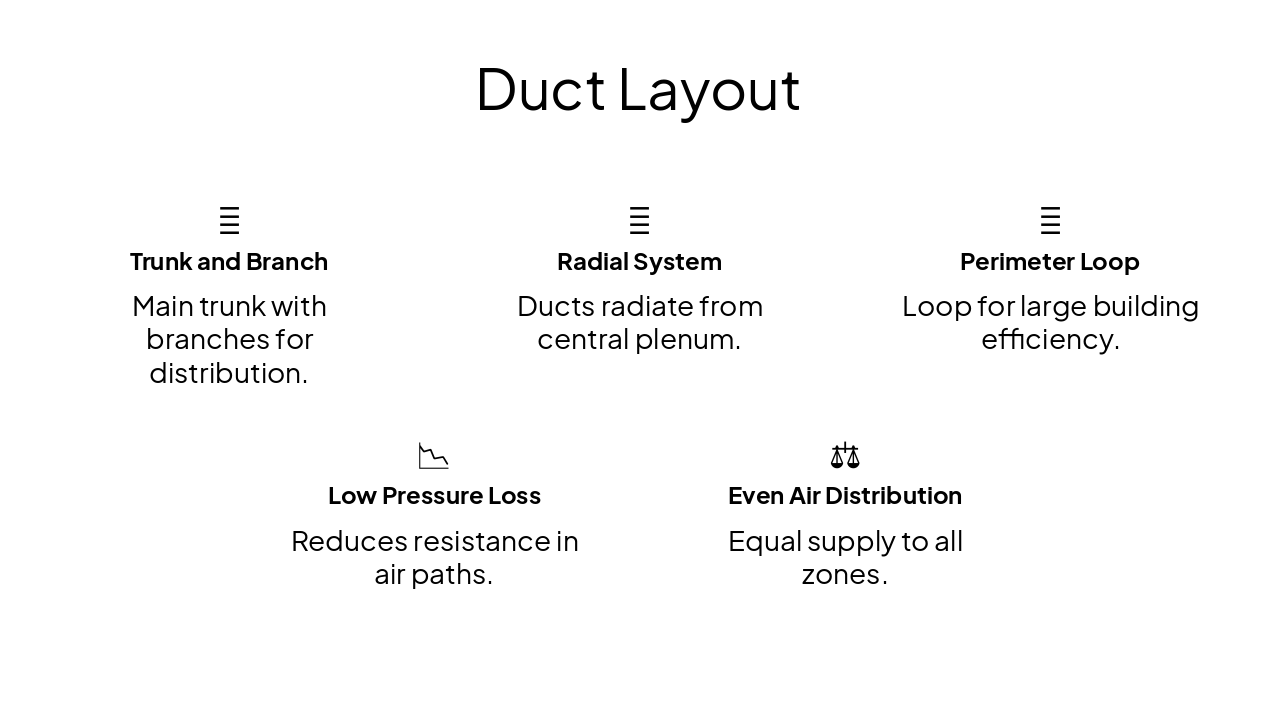
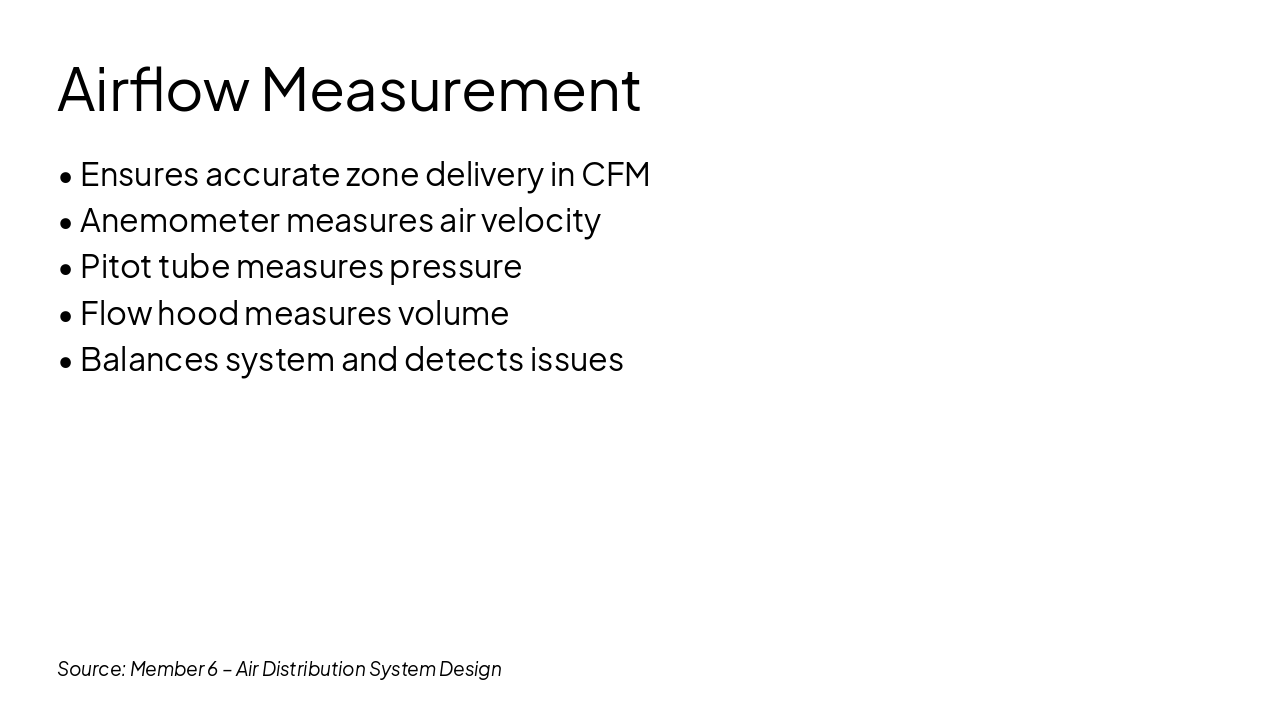
Duct Design • Airflow Measurement • Fans/Blowers • Diffusers and Grilles
Presented by: [Your Name] | Course: [Insert course name]
Source: HVAC Presentation Outline