Slide 1 - 포트폴리오 표지
This is a portfolio cover title slide titled "포트폴리오 표지." It displays the main text "Automation Meets Creativity" with a subtitle showing a name and "로봇공학 전공" for robotics major.
Automation Meets Creativity
[이름] 로봇공학 전공

Generated from prompt:
로봇공학 석사용 면접 포트폴리오 30페이지 구성. 블루 계열의 테크 감성 스타일로 디자인. 1~3. INTRO 1. 표지 — 이름, 전공, 한 줄 슬로건 (“Automation Meets Creativity”) 2. 소개 — 학력, 관심 연구 분야, 비전 3. 포트폴리오 개요 — 전체 목차 및 핵심 주제 요약 4~7. ACADEMIC BACKGROUND 4. 학부 전공 과정 — 주요 수강 과목 및 프로젝트 5. 로봇공학 기초역량 — ROS, 제어, 센서, AI, Vision 등 6. 기술 스택 다이어그램 — Python, C++, PLC, SolidWorks 등 시각화 7. 연구 관심 분야 — 지능형 자동화, 협동로봇, AI 제어 8~13. AUTOMATION PROJECTS (학부시절 과제 중심) 8. 프로젝트 개요 (“Smart Automation for Efficiency”) 9. 문제 정의 & 목표 10. 시스템 아키텍처 / 설계도 11. 제어 알고리즘 / 코드 일부 시각화 12. 결과 및 개선점 13. 실험 영상 캡처 & 데이터 그래프 14~19. 삼성중공업 DT 인재교육 14. 교육 개요 및 목적 15. DT 교육 커리큘럼 요약 — 데이터 분석, IoT, 디지털 트윈 등 16. 팀 프로젝트 주제 및 역할 17. 사용 기술 및 툴 (Python, TensorFlow, OPC-UA 등) 18. 성과 및 배운 점 19. 피드백 & 수료 인증 이미지 20~26. 삼성중공업 자동화 프로젝트 20. 프로젝트 개요 (“Shipyard Automation System”) 21. 현장 분석 & 문제 정의 22. 제안한 솔루션 개요 23. 로봇 제어 시스템 구성도 24. 데이터 흐름 & 자동화 알고리즘 25. 결과 및 성과지표 26. 향후 개선 방향 27~30. CLOSING & VISION 27. 기술적 성장 요약 — Timeline 그래프 28. 진로 방향 / 연구 목표 29. 감사의 글 / Mentor 언급 30. Contact & QR Portfolio Link
35-slide portfolio for robotics master's interview showcasing academic background (ROS, AI, control), undergrad automation projects, Samsung Heavy Industries DT training & shipyard automation system,
This is a portfolio cover title slide titled "포트폴리오 표지." It displays the main text "Automation Meets Creativity" with a subtitle showing a name and "로봇공학 전공" for robotics major.
[이름] 로봇공학 전공

The slide, titled "소개" (Introduction), states the presenter's bachelor's degree in robotics from university. It highlights their interest in intelligent robots and AI control research, plus a vision to lead future industries through automation innovation.

This Portfolio Overview agenda slide outlines the presentation structure across key sections. It covers academic background (Slides 4-7), undergraduate automation projects (8-13), Samsung DT Talent Education (14-19), shipyard automation project (20-26), and closing vision (27-30).
Core coursework, skills, and research interests (Slides 4-7)
Smart systems for efficiency with results (Slides 8-13)
Data, IoT, digital twin training and team project (Slides 14-19)
Real-world robot control solution at Samsung (Slides 20-26)
Growth timeline, goals, and contact (Slides 27-30) Source: Robotics Master's Interview Portfolio

This slide serves as the section header for "ACADEMIC BACKGROUND" (section 04). Its subtitle outlines coverage from undergraduate major courses to research interests.
04
From undergraduate major courses to research interests

This slide, titled "Undergraduate Major Courses," lists key robotics classes. It covers robot dynamics and kinematics basics, PID control and stabilization, machine vision for image processing, mobile robot navigation projects, and IMU-LiDAR sensor fusion.

This slide, titled "로봇공학 기초역량" (Robotics Basic Competencies), presents a feature grid of four core robotics skills. It covers ROS mastery for scalable apps, PID & MPC control for dynamics, LiDAR-IMU fusion for localization, and CNN-YOLO for real-time vision.
{ "features": [ { "icon": "🤖", "heading": "ROS Mastery", "description": "Proficient in Robot Operating System for developing scalable robot applications." }, { "icon": "⚙️", "heading": "PID & MPC Control", "description": "Implemented PID controllers and Model Predictive Control for precise robot dynamics." }, { "icon": "📡", "heading": "LiDAR & IMU Sensors", "description": "Expert in fusing LiDAR and IMU data for accurate localization and mapping." }, { "icon": "🧠", "heading": "CNN & YOLO Vision", "description": "Built CNN models and YOLO detectors for real-time object recognition in robotics." } ] }

The slide is a technology stack diagram outlining four layers: High-Level Logic (Python with ROS2/Gazebo), Real-Time Processing (C++ with ROS2 bridges), Industrial Control (PLC with OPC-UA/EtherCAT), and Mechanical Design (SolidWorks with ROS2 simulation). Each layer specifies key functions and integrations for a robotics or automation workflow.
{ "headers": [ "Layer", "Technology", "Key Functions", "Integration" ], "rows": [ [ "High-Level Logic", "Python", "ROS2 Nodes, AI/ML Scripting", "ROS2, Gazebo" ], [ "Real-Time Processing", "C++", "Performance Optimization, Drivers", "ROS2 Bridges" ], [ "Industrial Control", "PLC", "Hardware I/O, Safety Control", "OPC-UA, EtherCAT" ], [ "Mechanical Design", "SolidWorks", "CAD Modeling, URDF Export", "ROS2 Simulation" ] ] }

This slide lists research interests under the title "연구 관심 분야" (Research Interests). It highlights intelligent automation for maximizing production efficiency and smart manufacturing, collaborative robots (cobots) for safe human-robot collaboration, and AI-based control systems for adaptive robot motion optimization.

This slide serves as the section header for Section 08 titled "AUTOMATION PROJECTS." It includes the subtitle "Undergraduate Smart Automation Projects for Enhanced Efficiency."
08
Undergraduate Smart Automation Projects for Enhanced Efficiency

This title slide, named "프로젝트 개요" (Project Overview), features the main text "Smart Automation for Efficiency." The subtitle reads "효율적 자동화 시스템 개발," meaning "Development of an Efficient Automation System."
효율적 자동화 시스템 개발
Source: Smart Automation for Efficiency Portfolio

The slide highlights problems like high manual labor dependency reducing production efficiency, frequent human errors, and safety risks from repetitive tasks. It sets goals for 30% efficiency gains through automation, error minimization, work standardization, and cost savings via process optimization.

This slide outlines a ROS-based system architecture workflow across four phases: Sensor Input (Camera, LiDAR, IMU publishing to /sensordata), Perception & Planning (processing to /plannedpath), Control (to /controlcmd), and Actuator Output (to hardware). Each phase lists key components, data flows via ROS topics, and associated nodes like sensorpublishernode and controlnode.
{ "headers": [ "Phase", "Key Components", "Data Flow", "ROS Nodes" ], "rows": [ [ "Sensor Input", "Camera, LiDAR, IMU", "Raw Signals → /sensordata", "sensorpublishernode" ], [ "Perception & Planning", "Computer Vision, Path Planner", "/sensordata → /plannedpath", "perceptionnode, plannernode" ], [ "Control", "PID Controller, Motion Control", "/plannedpath → /controlcmd", "controlnode" ], [ "Actuator Output", "Motors, Grippers, Servos", "/controlcmd → Hardware Execution", "actuatordriver_node" ] ] }
Source: ROS Node-based Robot Control Architecture

The slide visualizes a Python PID control algorithm with Kp, Ki, and Kd tuning parameters. It features a control loop flowchart (error → PID → actuator), real-time robot simulation stability, and code snippets emphasizing error accumulation and derivative calculations.
Source: Wikipedia PID Controller & Custom Python Snippet

The slide "결과 및 개선점" showcases key stats: a +25% efficiency improvement boosting process speed and a -40% error rate reduction decreasing operational failures. It also highlights the implementation of real-time learning via an adaptive AI module.
Boosted overall process speed
Decreased operational failures
Added adaptive AI module

The slide shows screenshots from experiment videos capturing key robot motion scenes. It includes a performance graph of time versus efficiency trends, demonstrating a 25% efficiency improvement and shortened cycle time.
Source: Wikipedia

This slide serves as the section header for Section 14, titled "Samsung Heavy Industries DT Talent Education." The subtitle describes participation experiences and major achievements in Digital Transformation (DT) education programs.
14
디지털 트랜스포메이션(DT) 교육 프로그램 참여 경험 및 주요 성과
Source: 로봇공학 석사용 면접 포트폴리오

This slide, titled "Education Overview and Purpose," specifies the training period as [기간]. It aims to strengthen shipyard DT capabilities while targeting the fostering of future talents.

The slide summarizes the DT education curriculum in a table covering three fields: Data Analysis, IoT, and Digital Twin. It lists key contents—data processing/visualization (Python, Pandas, Matplotlib), sensor connection/data collection (AWS IoT, OPC-UA), and virtual modeling/simulation (Unity, 3D Rendering)—alongside relevant technologies/tools.
{ "headers": [ "분야", "주요 내용", "기술/도구" ], "rows": [ [ "데이터 분석", "데이터 처리 및 시각화", "Python, Pandas, Matplotlib" ], [ "IoT", "센서 연결 및 데이터 수집", "AWS IoT, OPC-UA" ], [ "디지털 트윈", "가상 모델링 및 시뮬레이션", "Unity, 3D Rendering" ] ] }
Source: 삼성중공업 DT 인재교육

The slide outlines the team project on a Ship Production IoT Monitoring System, with the presenter's role as Algorithm Development Team Leader. Key responsibilities include designing real-time data analysis algorithms, leading IoT data integration and optimization, and aiming to improve production efficiency and quality.
Source: 삼성중공업 DT 인재교육

This slide, titled "사용 기술 및 툴" (Technologies and Tools Used), features a grid highlighting four key technologies: Python for automation scripts and data analysis, TensorFlow for machine learning models and AI control systems, OPC-UA for real-time industrial data exchange, and MQTT for efficient IoT pub/sub messaging. Each entry includes an icon and a concise description of its primary application.
{ "features": [ { "icon": "🐍", "heading": "Python 프로그래밍", "description": "자동화 스크립트, 데이터 처리 및 분석 구현에 핵심 활용." }, { "icon": "🧠", "heading": "TensorFlow 프레임워크", "description": "기계학습 모델 개발과 AI 기반 제어 시스템 적용." }, { "icon": "🔌", "heading": "OPC-UA 통신", "description": "산업 설비 간 실시간 데이터 교환 및 통합 표준." }, { "icon": "📡", "heading": "MQTT 프로토콜", "description": "경량 IoT 메시징을 위한 효율적인 pub/sub 통신." } ] }
Source: 삼성중공업 DT 인재교육

The slide highlights key achievements, including the successful completion of the Shipyard DT prototype, strengthened multidisciplinary team collaboration, adherence to data ethics principles, and a 20% efficiency gain via simulation. It also notes lessons learned, such as insights into scalable automation solutions.

The slide "Feedback & Completion Certification" highlights positive instructor feedback on project innovativeness and excellent completion of all Digital Twin training modules. It also features the official Samsung Heavy Industries DT Talent Education certificate and recognition of robot automation skills.
Source: Professional certification

This section header slide, titled "Samsung Heavy Industries Automation Project," marks Section 22. It presents the "Overview of Proposed Solution" with a subtitle on intelligent automation solutions to optimize shipyard welding and assembly processes.
22
Intelligent automation solutions to optimize shipyard welding and assembly processes
Source: Shipyard 실무 프로젝트

This title slide, labeled "프로젝트 개요" (Project Overview), presents the main title "Shipyard Automation System." The subtitle in Korean reads "조선소 자동화 솔루션," highlighting a shipyard automation solution.
조선소 자동화 솔루션
Source: Shipyard Automation System 조선소 자동화 솔루션

The slide analyzes on-site block movement, dominated by manual handling of heavy objects. It highlights problems like high accident risks (falls, collisions), low efficiency and productivity, worker fatigue from repetitive labor, and challenging conditions such as narrow spaces and poor visibility.

The slide outlines the proposed solution introducing AGV robots for automated material transport. It highlights AI-based path optimization, real-time obstacle avoidance, seamless PLC integration, and scalable fleet management.

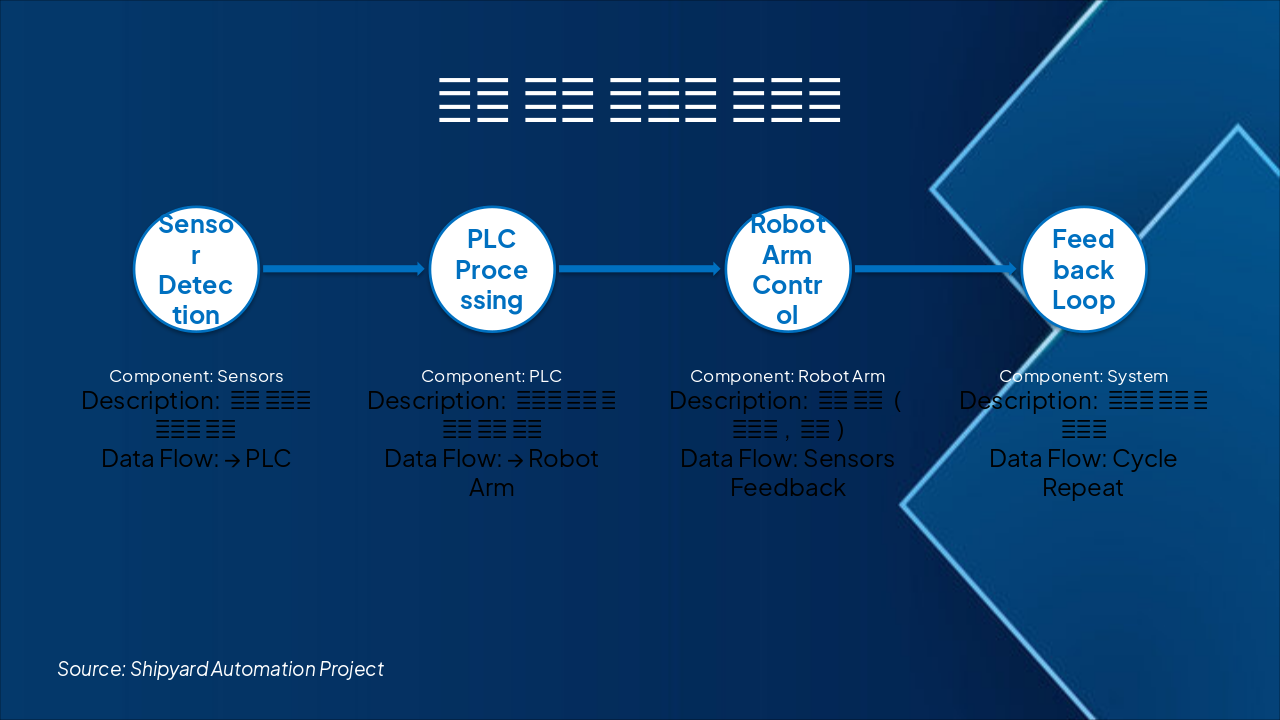
The slide outlines a robot control system workflow: sensors collect real-time environmental data and send it to the PLC for analysis and command generation, which directs the robot arm to execute tasks like movement and manipulation. A feedback loop from the robot arm to sensors enables real-time adjustments, optimization, and cycle repetition.
{ "headers": [ "Step", "Component", "Description", "Data Flow" ], "rows": [ [ "Sensor Detection", "Sensors", "환경 데이터 실시간 수집", "→ PLC" ], [ "PLC Processing", "PLC", "데이터 분석 및 제어 명령 생성", "→ Robot Arm" ], [ "Robot Arm Control", "Robot Arm", "작업 실행 (움직임, 조작)", "Sensors Feedback" ], [ "Feedback Loop", "System", "실시간 조정 및 최적화", "Cycle Repeat" ] ] }
Source: Shipyard Automation Project
The workflow depicts shipyard data flow starting with real-time IoT sensor acquisition via OPC-UA and MQTT, followed by secure cloud storage using AWS IoT Core and Kafka. It then executes AI/ML automation with Python and TensorFlow for control decisions, ending with command dispatch to robots and PLCs via OPC-UA and REST APIs.
{ "headers": [ "Stage", "Description", "Technologies", "Output" ], "rows": [ [ "IoT Data Acquisition", "Real-time data collection from shipyard sensors and equipment", "IoT Sensors, OPC-UA, MQTT", "Raw Data Stream" ], [ "Cloud Ingestion & Storage", "Secure upload and storage of data in cloud platform", "AWS IoT Core, Kafka", "Processed Data in Cloud" ], [ "Automation Algorithm Execution", "AI/ML analysis for decision-making and optimization", "Python, TensorFlow, Custom Algorithms", "Control Decisions" ], [ "Command Dispatch", "Issuance of control signals to robots and PLCs", "OPC-UA, REST APIs", "Executed Control Commands" ] ] }
Source: IoT 데이터 → 클라우드 → 제어 명령

The slide showcases key results with a 35% productivity increase, 99.5% system uptime, and 28% cost savings. It also reports zero safety incidents throughout the project.
Overall efficiency boosted by 35%
Zero accidents throughout project
Achieved near-perfect operational reliability
Reduced operational expenses significantly Source: Samsung Heavy Industries Shipyard Automation Project

Future improvements include 5G integration for real-time low-latency communication and multi-robot collaboration systems. Further enhancements involve AI predictive maintenance, edge computing for data optimization, and digital twin expansion for advanced simulations.

This section header slide is titled "Closing & Vision" and spans sections 27-30. Its subtitle highlights wrapping up achievements and envisioning the future in robotics.
27-30
Wrapping up achievements and envisioning the future in robotics
Source: 로봇공학 석사용 면접 포트폴리오

This timeline summarizes technical growth from 2020-2024, starting with undergraduate ROS foundation in robotics skills (2020-2022) and Samsung DT training in IoT, data analysis, and digital twins (2023 Q1-Q2). It progresses to PLC programming for shipyard automation (2023 Q3) and full PLC-based system deployment for industrial robotics efficiency (2024).
2020-2022: Undergraduate ROS Foundation Developed core robotics skills with ROS, control, sensors, and vision systems. 2023 Q1-Q2: DT Talent Education Program Completed Samsung DT training in IoT, data analysis, and digital twins. 2023 Q3: PLC Practical Training Start Transitioned to real-world PLC programming for shipyard automation. 2024: Full Automation Integration Deployed PLC-based systems enhancing efficiency in industrial robotics.

The slide outlines a master's focus on collaborative robot AI research, aiming to become an industrial innovation leader. Key goals include developing human-robot collaboration tech, commercializing intelligent automation systems, and advancing Industry 4.0 in shipbuilding.
Source: 로봇공학 석사용 면접 포트폴리오

This slide, titled "감사의 글" (Words of Gratitude), features a quote thanking a mentor for valuable advice and dedicated guidance that illuminated the author's robotics research journey. The quote, from [이름], a robotics master's applicant who completed Samsung Heavy Industries DT Talent Education, notes that this portfolio is part of that mentorship's fruit.
> 멘토님의 지도에 감사드립니다. 귀중한 조언과 헌신적인 지도로 로봇공학 연구 여정을 밝혀주신 멘토님께 깊은 감사의 마음을 전합니다. 이 포트폴리오가 그 열매의 일부입니다.
— [이름], 로봇공학 석사 과정 지원자 (삼성중공업 DT 인재교육 수료)
Source: 로봇공학 석사 면접 포트폴리오

This title slide is named "Contact & QR." It features contact details including an email, LinkedIn link, and a QR code for portfolio download.
Email: [이메일] | LinkedIn: [링크] | QR: 포트폴리오 다운로드
Source: 로봇공학 석사용 면접 포트폴리오

Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.