Slide 1 - Image Classification with CNNs
This is a title slide for a presentation on "Image Classification with CNNs." It features the subtitle "University Project" along with placeholders for "Your Name, Date."
University Project
Your Name, Date

Generated from prompt:
A 15-slide presentation titled 'Image Classification with CNNs' for a university project in computer vision. The slides include: 1) Title and intro, 2) Motivation & Goal, 3) Dataset overview (Oxford-IIIT Pets), 4) Preprocessing, 5) CNN Basics, 6) Transfer Learning, 7) Models Used, 8) Custom CNN, 9) Training Setup, 10) Training Curves, 11) Confusion Matrices, 12) Performance Comparison, 13) Key Findings, 14) Limitations & Future Work, and 15) Conclusion. Each slide includes both short bullet points (for slide text) and a speaker script for presentation delivery. The design should be clean, academic, and visual, with consistent layout and modern color palette.
University project presentation on classifying 37 pet breeds from Oxford-IIIT Pets dataset using CNNs. Covers preprocessing, basics, transfer learning (VGG/ResNet), custom CNN, training curves, confus
This is a title slide for a presentation on "Image Classification with CNNs." It features the subtitle "University Project" along with placeholders for "Your Name, Date."
Your Name, Date

Accurate pet breed identification is vital for vets and apps, motivating the goal to build and train CNNs on 37 breeds. The target is over 80% accuracy, comparing custom versus transfer learning models.

The slide "Dataset Overview (Oxford-IIIT Pets)" features key statistics on the left: 7,349 images across 37 cat and dog breeds (~200 per breed) with fine head/pose annotations. The right side displays diverse sample images highlighting breed variations in appearance and poses for robust training.
| Key Statistics | Sample Images |
|---|
| 7,349 images 37 breeds (cats & dogs) ~200 images per breed Fine annotations (head/pose masks) | Diverse examples of cat and dog breeds from the dataset, highlighting variations in appearance and poses for robust training. |
Source: Oxford-IIIT Pets Dataset

The Preprocessing workflow slide outlines steps for handling raw Oxford-IIIT Pets images. It covers resizing to 224x224, normalizing pixels to [0,1], augmenting with rotations/flips for variety and class balance, and converting to framework tensors like PyTorch.
{ "headers": [ "Step", "Operation", "Details" ], "rows": [ [ "Raw", "Input", "Original Oxford-IIIT Pets images" ], [ "Resize", "Scale", "To 224x224 (standard CNN input)" ], [ "Normalize", "Scale pixels", "To [0,1] range for stability" ], [ "Augment", "Apply transformations", "Rotation/Flip to add variety & balance classes" ], [ "Tensors", "Convert", "To framework tensors (e.g., PyTorch)" ] ] }
Source: Workflow: Raw → Resize(224x224) → Normalize → Augment(Rot/Flip) → Tensors

CNN Basics slide outlines key components: convolutional layers extract features like edges and textures, pooling layers downsample spatial dimensions, and fully connected layers classify via softmax probabilities. ReLU activation introduces non-linearity, while backpropagation trains network weights.
Source: Image Classification with CNNs

This slide on Transfer Learning shows an image with key steps: freeze the pretrained base and fine-tune the classifier. It emphasizes that this method needs fewer data and epochs.
Source: Wikipedia - Transfer learning

The "Models Used" slide features a grid showcasing four key models: VGG16 Backbone with ImageNet-pretrained convolutions, ResNet50 Residuals using skip connections for deep training, EfficientNet Transfer for balanced accuracy and efficiency, and a Custom CNN optimized for pet classification. Each entry includes an icon and a concise description of its strengths.
{ "features": [ { "icon": "🧱", "heading": "VGG16 Backbone", "description": "Deep stacked convolutions pretrained on ImageNet for features." }, { "icon": "🔗", "heading": "ResNet50 Residuals", "description": "Skip connections enable very deep network training." }, { "icon": "⚡", "heading": "EfficientNet Transfer", "description": "Balances accuracy, efficiency using transfer learning." }, { "icon": "🔧", "heading": "Custom CNN Design", "description": "Tailored architecture optimized for pet classification." } ] }

The Custom CNN slide depicts a neural network architecture with three convolutional blocks (64-128-256 filters), each followed by max pooling. It concludes with two fully connected layers (512-37 neurons) and dropout at a rate of 0.5.
Source: Wikipedia

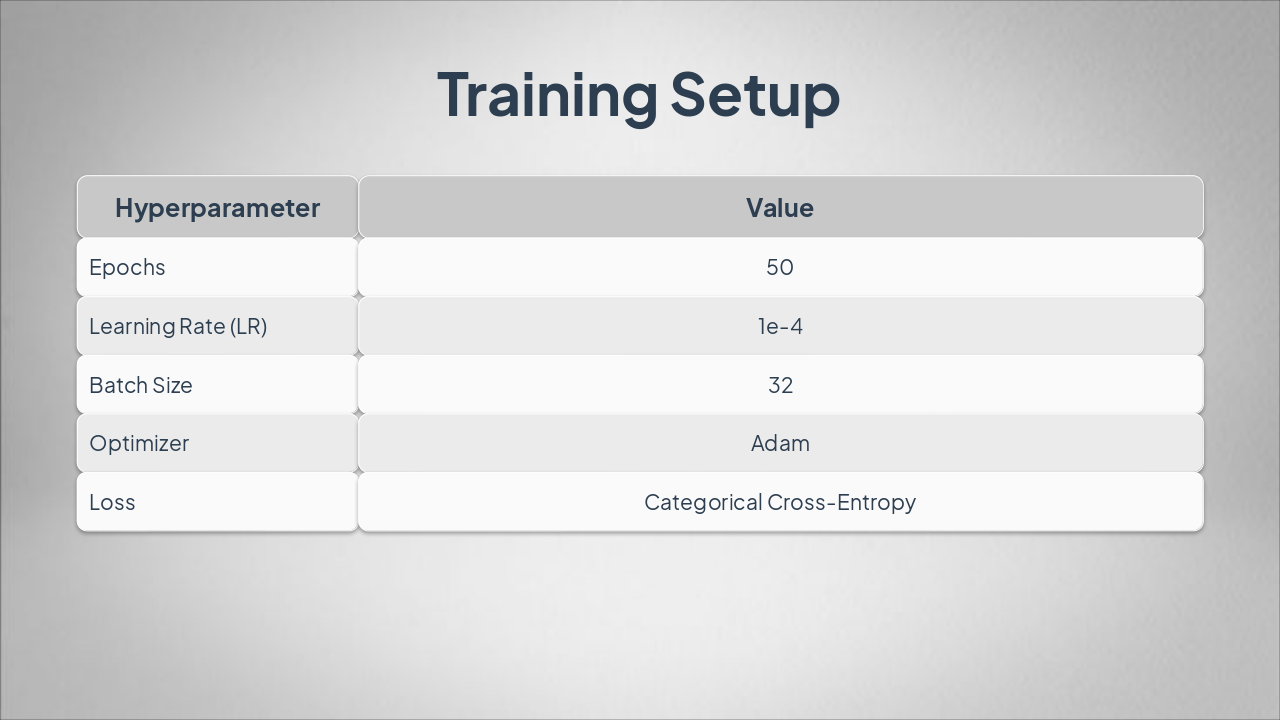
The "Training Setup" slide outlines key hyperparameters in a table format. It specifies 50 epochs, a 1e-4 learning rate, batch size of 32, Adam optimizer, and Categorical Cross-Entropy loss.
{ "headers": [ "Hyperparameter", "Value" ], "rows": [ [ "Epochs", "50" ], [ "Learning Rate (LR)", "1e-4" ], [ "Batch Size", "32" ], [ "Optimizer", "Adam" ], [ "Loss", "Categorical Cross-Entropy" ] ] }
The Training Curves slide reports a peak validation accuracy of 82% for the from-scratch model and 89% for VGG transfer learning using pre-trained weights. Overfitting risk is low, mitigated by dropout layers.
Peak for from-scratch model
Boost from pre-trained weights
Mitigated by dropout layers

The slide displays confusion matrices for VGG and ResNet on cat breed classification. VGG and ResNet excel on similar breeds like Siamese and Persian, with errors in fine-grained distinctions and VGG showing the strongest diagonal performance in heatmaps.
Source: Confusion matrix

The "Performance Comparison" slide features a table comparing Top-1 and Top-5 accuracies across three models. ResNet leads with 91.2% Top-1 and 99% Top-5, followed by VGG16 at 89.3% and 98%, and Custom at 82.1% and 95%.
{ "headers": [ "Model", "Top-1", "Top-5" ], "rows": [ [ "Custom", "82.1%", "95%" ], [ "VGG16", "89.3%", "98%" ], [ "ResNet", "91.2%", "99%" ] ] }

Transfer learning outperforms custom CNNs, deeper networks improve performance, and data augmentation prevents overfitting. The Pets dataset poses challenges for fine-grained recognition.

The slide highlights limitations such as a small dataset causing breed confusion, imbalance restricting performance, and unutilized animal poses. Future work proposes larger balanced datasets, Vision Transformers (ViT), and ensemble methods for state-of-the-art results.

The conclusion slide emphasizes that CNNs are powerful for images, transfer learning is efficient, and 91% accuracy was achieved on the Pets dataset. It concludes with an invitation for Q&A.
• CNNs powerful for images
Q&A?

Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.