Slide 1 - Emphysema in Pediatrics
Emphysema in Pediatrics
Presented by Gauri Narkar Roll No: 92
---
Photo by Annie Spratt on Unsplash

Generated from prompt:
Create a clean, modern medical PowerPoint presentation titled "Emphysema in Pediatrics" with the following slides: 1. Title Slide: ONLY the title "Emphysema in Pediatrics" (no key focus areas, no subtitles). Include Presented by Gauri Narkar, Roll No: 92 in small professional formatting. 2. Definition 3. Classification – Based on Etiology 4. Classification – Based on Pathology (Panacinar, Centrilobular, Paraseptal, Irregular) 5. Etiology (Congenital, Acquired, Genetic – Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency) 6. Pathophysiology (Flow sequence diagram style) 7. Clinical Features (Infants CLE, Genetic Emphysema) 8. Investigations 9. Management – General & Medical 10. Management – Surgical 11. Complications Use a professional medical theme with subtle blue tones, clean layout, bullet formatting, and section divider slides.
Comprehensive overview of emphysema in children, covering definition, classifications (etiology & pathology), pathophysiology, clinical features, investigations, medical/surgical management, complications, and key takeaways for early diagnosis and多学科
Emphysema in Pediatrics
Presented by Gauri Narkar Roll No: 92
---
Photo by Annie Spratt on Unsplash

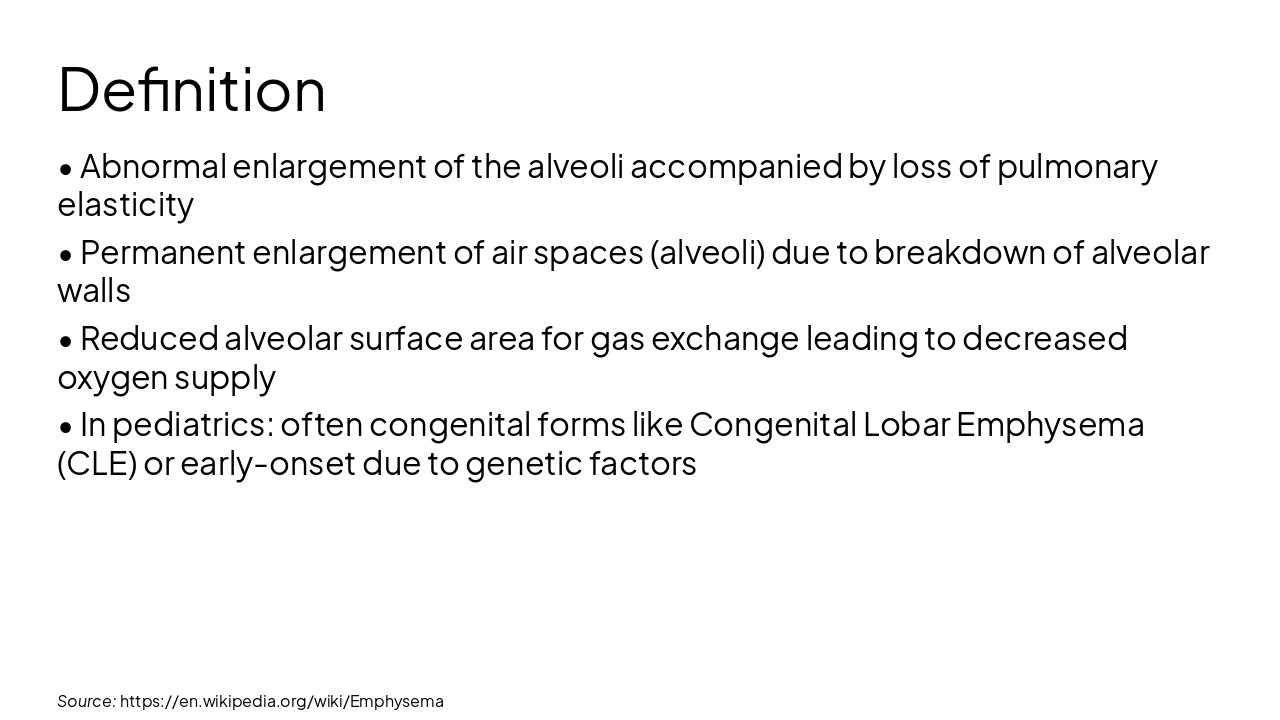
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema
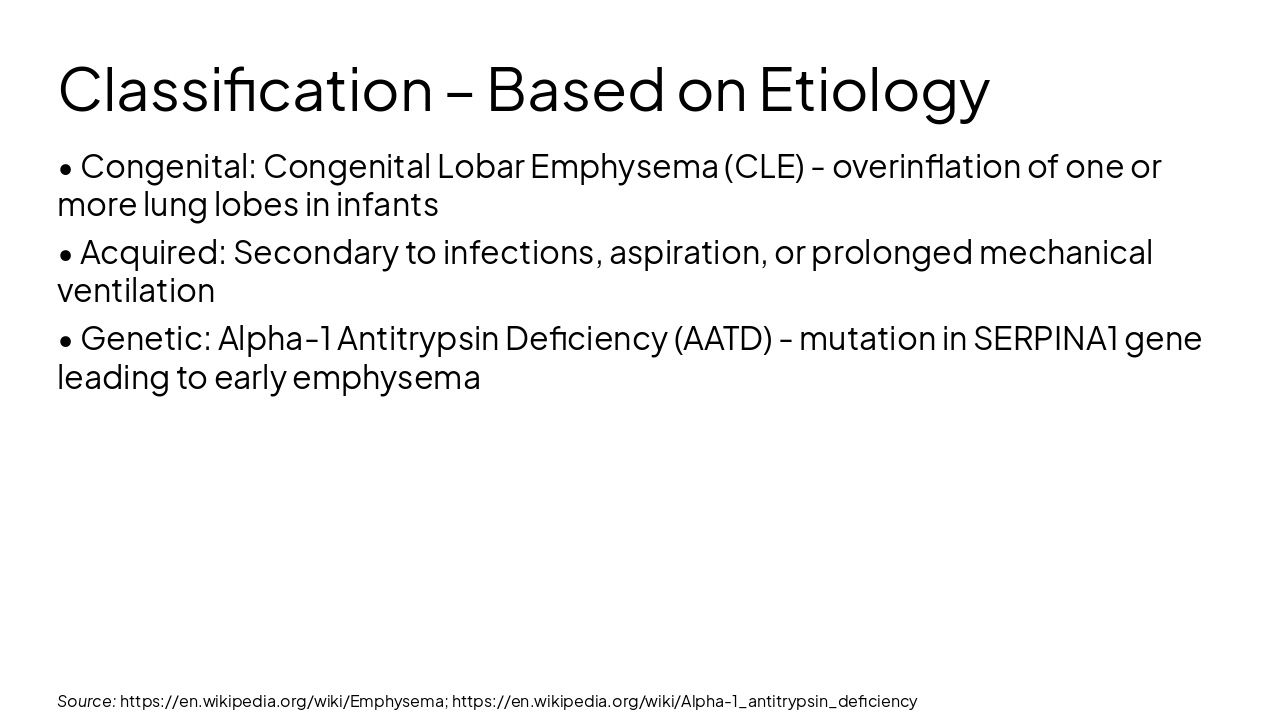
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-1_antitrypsin_deficiency
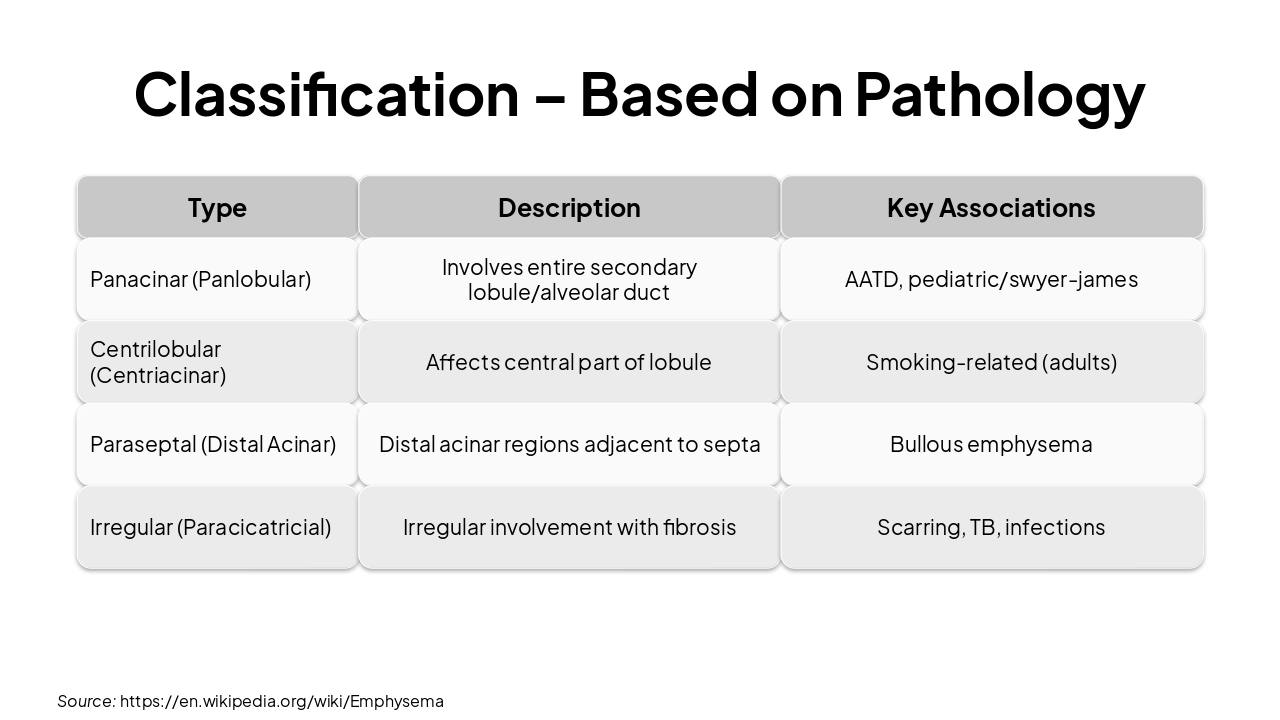
| Type | Description | Key Associations |
|---|---|---|
| Panacinar (Panlobular) | Involves entire secondary lobule/alveolar duct | AATD, pediatric/swyer-james |
| Centrilobular (Centriacinar) | Affects central part of lobule | Smoking-related (adults) |
| Paraseptal (Distal Acinar) | Distal acinar regions adjacent to septa | Bullous emphysema |
| Irregular (Paracicatricial) | Irregular involvement with fibrosis | Scarring, TB, infections |
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema
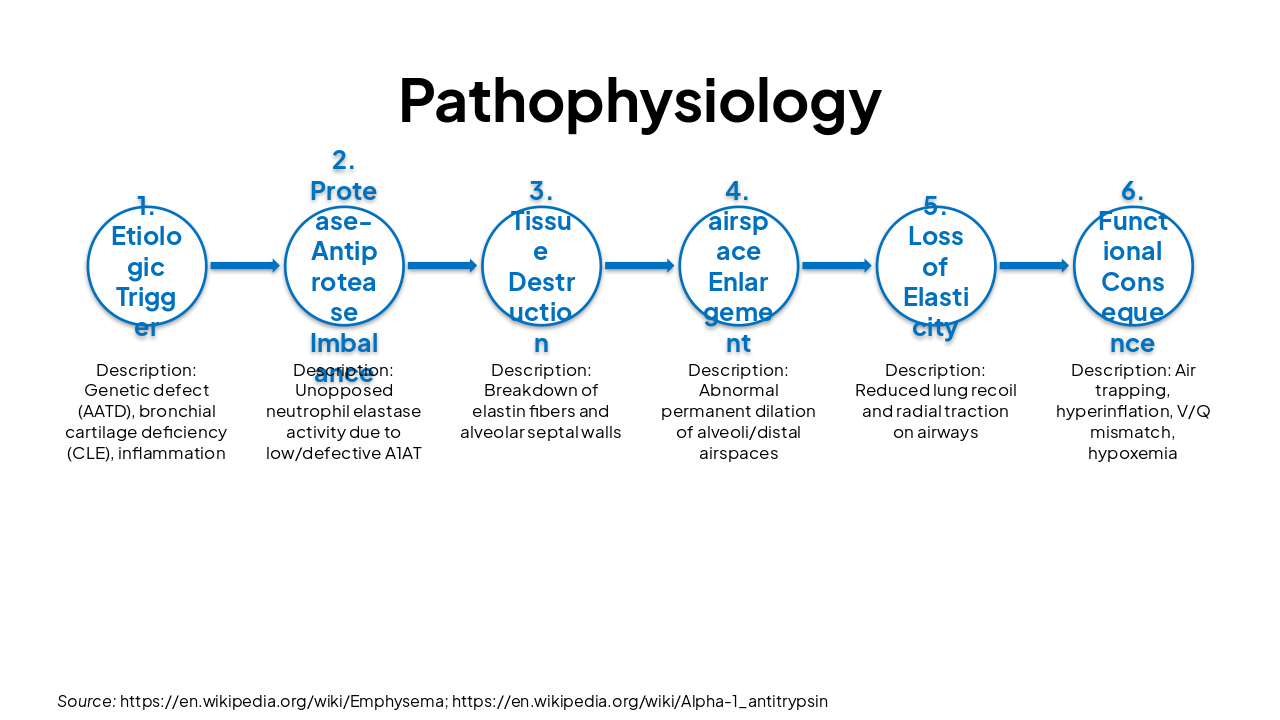
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-1_antitrypsin_deficiency; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Congenital_lobar_emphysema

| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Etiologic Trigger | Genetic defect (AATD), bronchial cartilage deficiency (CLE), inflammation |
| 2. Protease-Antiprotease Imbalance | Unopposed neutrophil elastase activity due to low/defective A1AT |
| 3. Tissue Destruction | Breakdown of elastin fibers and alveolar septal walls |
| 4. airspace Enlargement | Abnormal permanent dilation of alveoli/distal airspaces |
| 5. Loss of Elasticity | Reduced lung recoil and radial traction on airways |
| 6. Functional Consequence | Air trapping, hyperinflation, V/Q mismatch, hypoxemia |
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-1_antitrypsin
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-1_antitrypsin_deficiency; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema

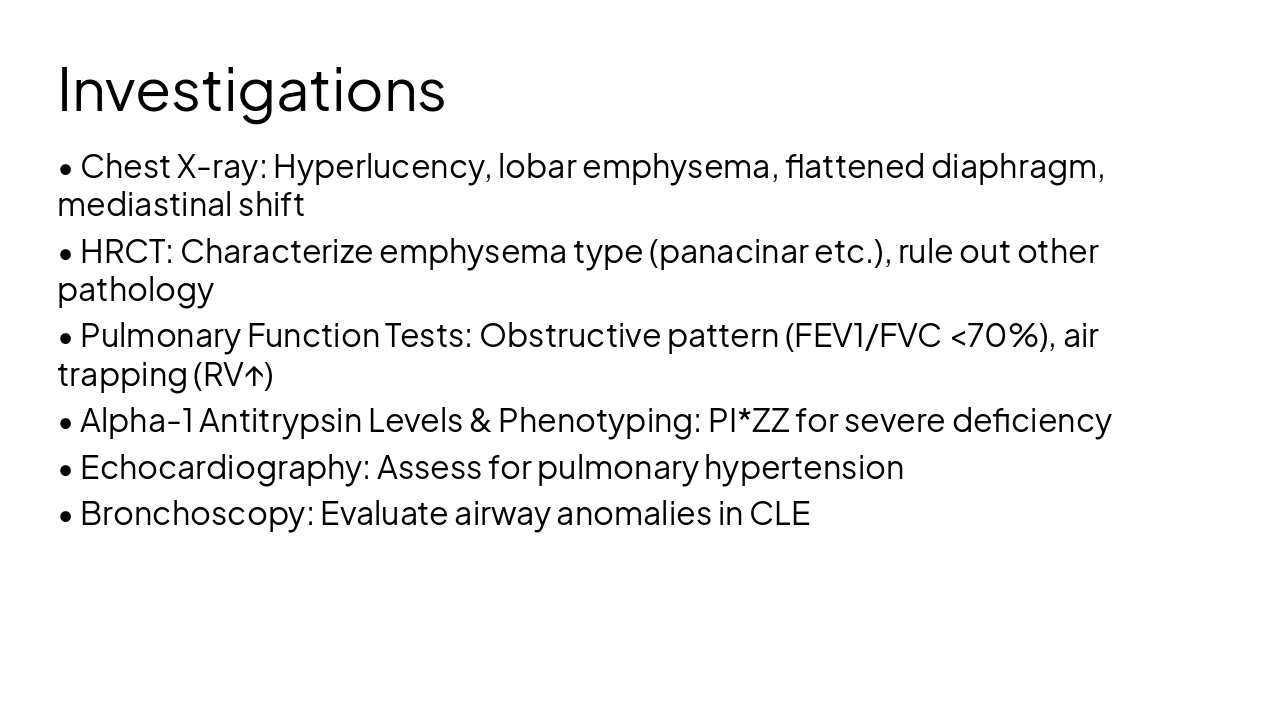
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-1_antitrypsin_deficiency
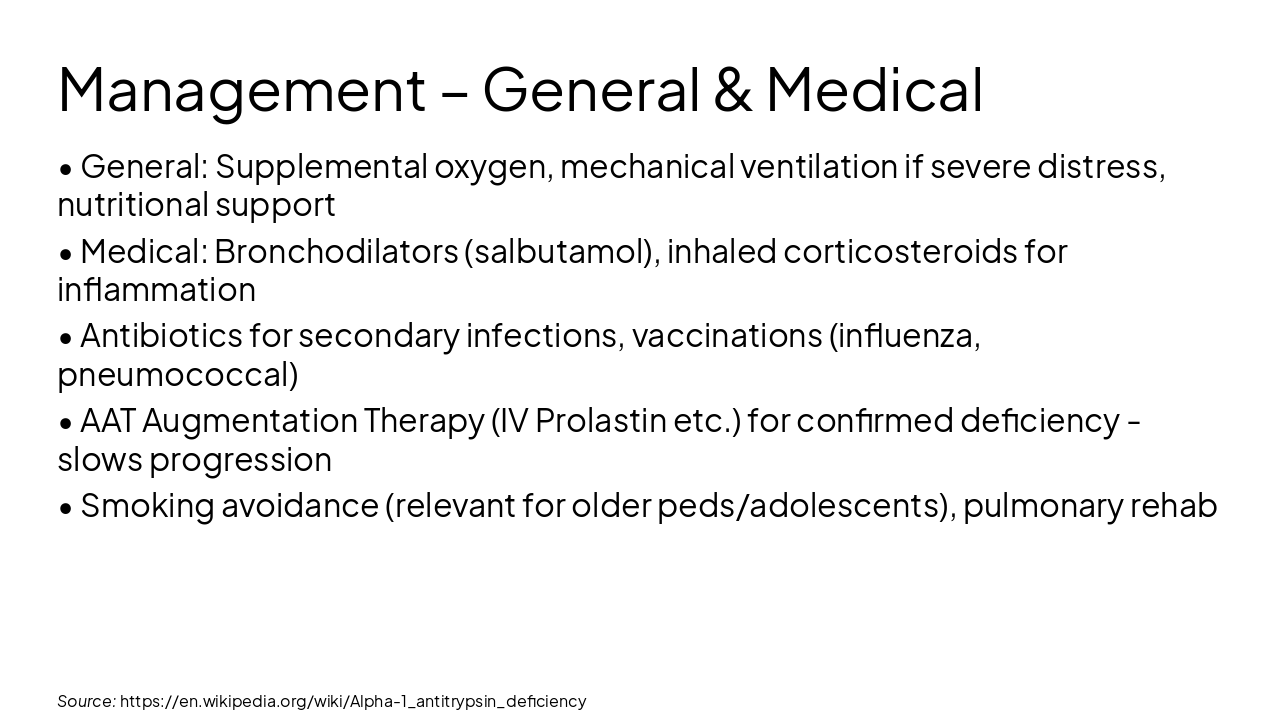
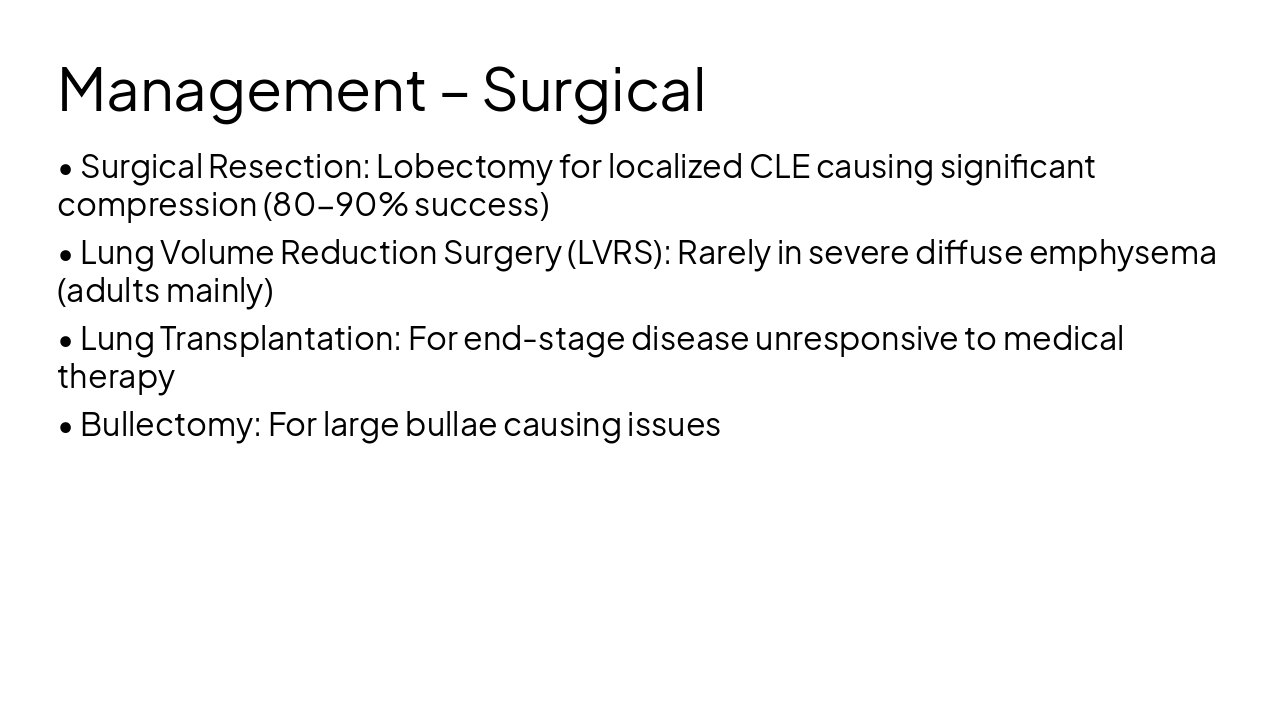
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emphysema; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-1_antitrypsin_deficiency

Key Takeaways: Early diagnosis and management crucial for pediatric emphysema Tailor approach to etiology (CLE vs AATD) Multidisciplinary care improves outcomes
Questions?
---
Photo by Etactics Inc on Unsplash

2
Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis
---
Photo by Maskmedicare Shop on Unsplash
Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.