Slide 1 - Emphysema in Pediatrics
Emphysema in Pediatrics
Presented by Gauri Narkar, Roll No: 92
---
Photo by Etactics Inc on Unsplash

Generated from prompt:
Create a clean, modern medical PowerPoint presentation titled "Emphysema in Pediatrics". 1. Title Slide: ONLY the title "Emphysema in Pediatrics" with Presented by Gauri Narkar, Roll No: 92 in small professional formatting. 2. Definition (Add a relevant medical illustration of alveolar enlargement) 3. Classification – Based on Etiology (Add relevant pediatric lung image) 4. Classification – Based on Pathology (Panacinar, Centrilobular, Paraseptal, Irregular) – include labeled structural diagram images 5. Etiology (Congenital, Acquired, Genetic – Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency) – include relevant diagram/image 6. Pathophysiology – flow sequence diagram style with visual arrows 7. Clinical Features – include relevant pediatric respiratory distress image (non-graphic, educational) 8. Investigations – include chest X-ray and CT scan example images 9. Management – General & Medical – include inhaler/oxygen therapy visuals 10. Management – Surgical – include simple lobectomy illustration 11. Complications – include simple lung complication illustration Use a professional medical theme with subtle blue tones, clean layout, bullet formatting, and high-quality educational medical images from slide 2 onward.
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of emphysema in pediatric patients, a rare condition often linked to congenital anomalies or genetic factors like Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD). It covers definitions, classifications by etI
Emphysema in Pediatrics
Presented by Gauri Narkar, Roll No: 92
---
Photo by Etactics Inc on Unsplash

---
Photo by Europeana on Unsplash
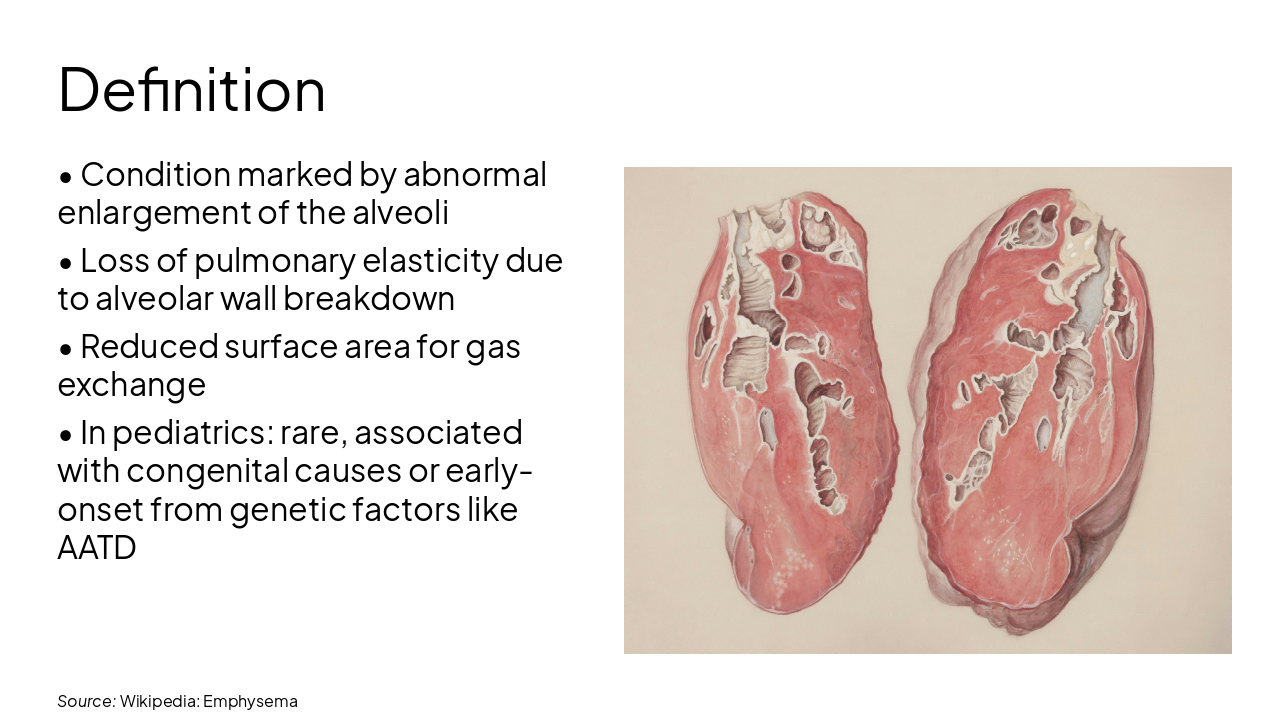
Source: Wikipedia: Emphysema
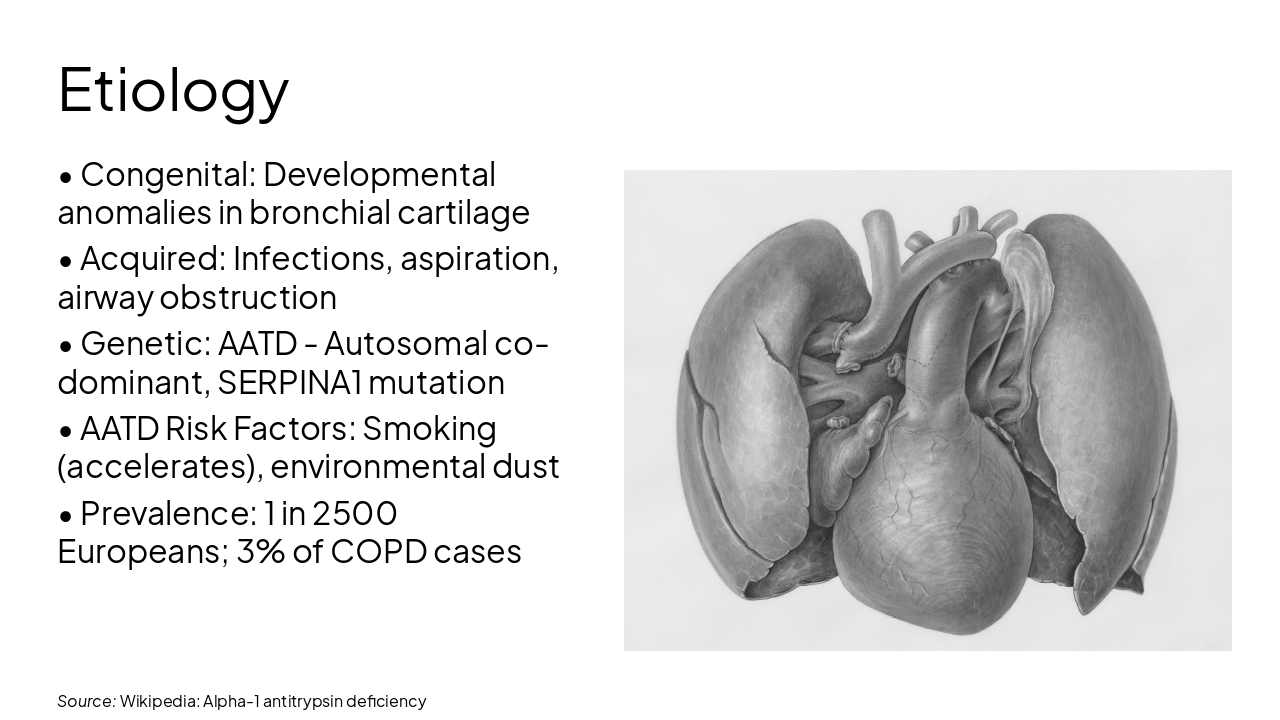
Source: Wikipedia: Emphysema, Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
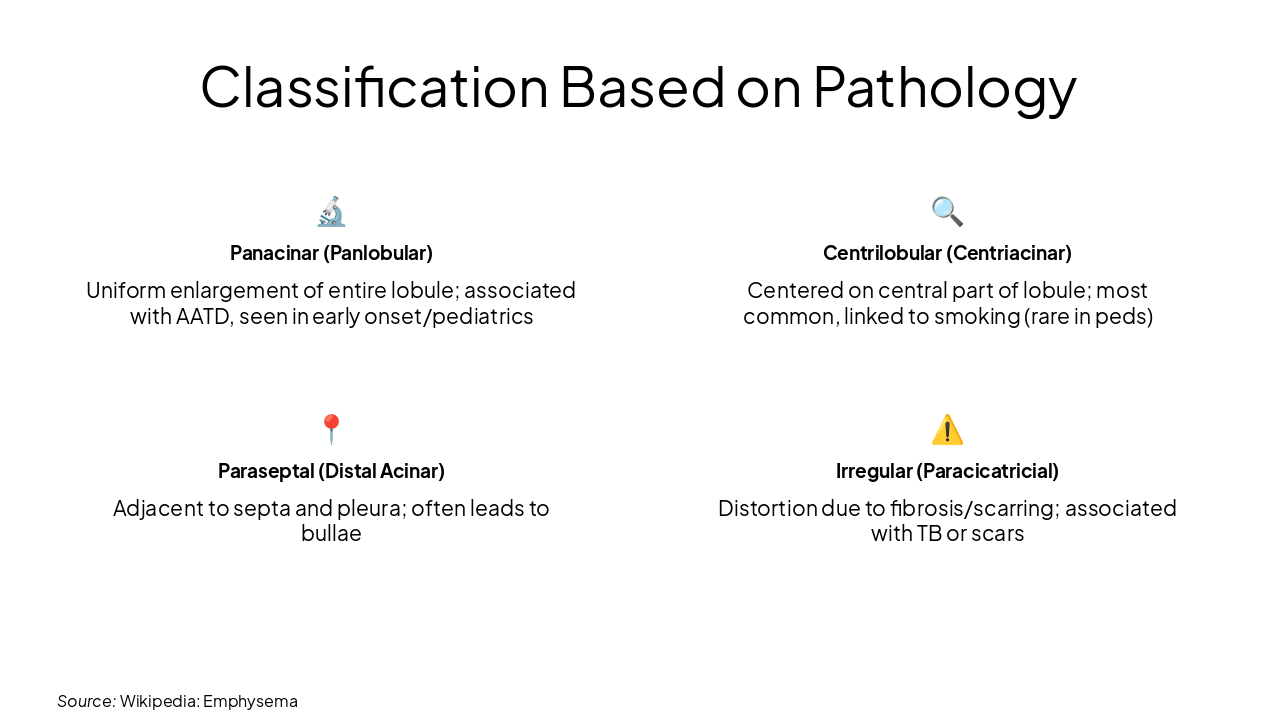
🔬 Panacinar (Panlobular) Uniform enlargement of entire lobule; associated with AATD, seen in early onset/pediatrics
🔍 Centrilobular (Centriacinar) Centered on central part of lobule; most common, linked to smoking (rare in peds)
📍 Paraseptal (Distal Acinar) Adjacent to septa and pleura; often leads to bullae
⚠️ Irregular (Paracicatricial) Distortion due to fibrosis/scarring; associated with TB or scars
Source: Wikipedia: Emphysema
---
Photo by Europeana on Unsplash
Source: Wikipedia: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
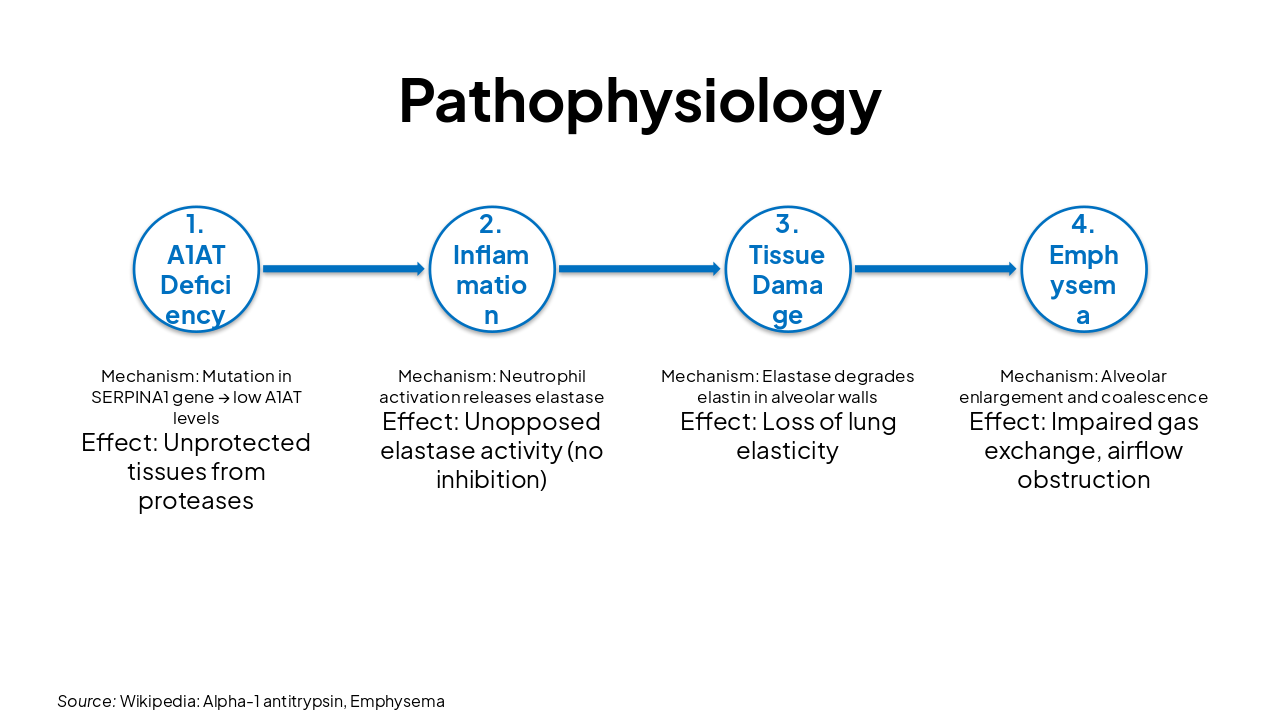
| Stage | Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| 1. A1AT Deficiency | Mutation in SERPINA1 gene → low A1AT levels | Unprotected tissues from proteases |
| 2. Inflammation | Neutrophil activation releases elastase | Unopposed elastase activity (no inhibition) |
| 3. Tissue Damage | Elastase degrades elastin in alveolar walls | Loss of lung elasticity |
| 4. Emphysema | Alveolar enlargement and coalescence | Impaired gas exchange, airflow obstruction |
Source: Wikipedia: Alpha-1 antitrypsin, Emphysema
---
Photo by Gabe Pierce on Unsplash
Source: Wikipedia: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency

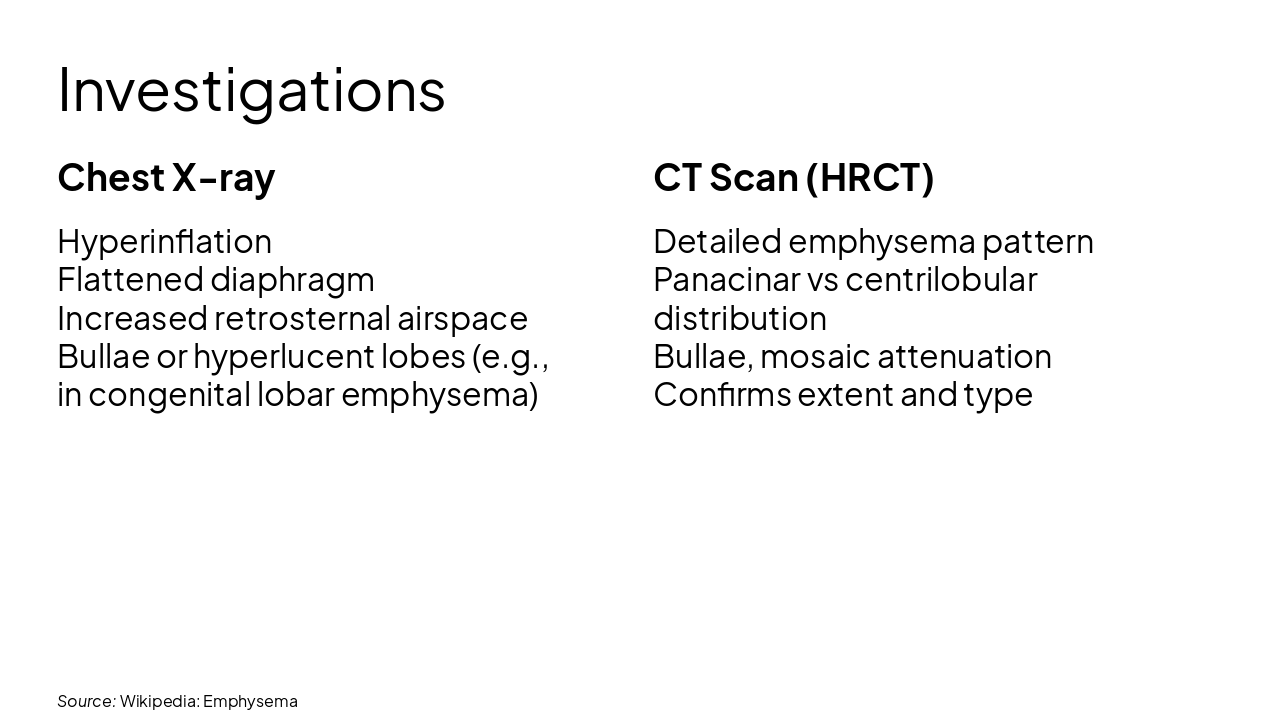
Chest X-ray Hyperinflation Flattened diaphragm Increased retrosternal airspace Bullae or hyperlucent lobes (e.g., in congenital lobar emphysema)
CT Scan (HRCT) Detailed emphysema pattern Panacinar vs centrilobular distribution Bullae, mosaic attenuation Confirms extent and type
Source: Wikipedia: Emphysema
---
Photo by Gabe Pierce on Unsplash
Source: Wikipedia: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency

---
Photo by Aakash Dhage on Unsplash
Source: Wikipedia: Emphysema, Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Emphysema in pediatrics is rare but serious, often congenital or genetic (AATD). Early diagnosis via imaging and management (medical/surgical) crucial. Augmentation therapy and lifestyle avoidance key for AATD.
Thank you! Questions?
---
Photo by Etactics Inc on Unsplash
Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.