Slide 1 - Class 11 Computer Science (CBSE 083, 2025-26)
Volume 1: Programming First Strategy PART 1
Chapters 1-8: Computational Thinking to Modules Strictly from Textbook - Detailed Concepts, Programs & Exercises
---
Photo by Pict4life on Unsplash

Generated from prompt:
Create PART 1 of a SINGLE MEGA COMBINED Presentation for Class 11 Computer Science (CBSE 083, 2025-26) strictly from the uploaded textbook /mnt/data/C11 COMP SC SSM FINAL 2025-26_2.pdf. This is Volume 1 (Programming First Strategy). Include ONLY these chapters fully extracted from the PDF: 1. Computational Thinking & Programming – I 2. Python Basics (Tokens, Identifiers, Variables, Data Types, Operators) 3. Flow of Control 4. Strings 5. Lists 6. Tuples 7. Dictionary 8. Modules STRICT RULES: - Use PDF as PRIMARY SOURCE. - Do NOT summarize. - Extract ALL definitions, examples, tables, programs, exercises, practicals. - 1 Concept = 1 Slide. - Minimum 180–220 slides in this volume. For EVERY concept slide include: - Simple meaning - Hinglish explanation (Devanshu Sir style) - Real life example - Step-by-step explanation - Analogy - Exam tip - Memory trick For EVERY program include: - Correct runnable Python code - Line-by-line explanation - Dry run table - Output - Common mistakes - Practice task For EVERY chapter include: - 5 MCQs - 5 Short Answer - 2 Long Answer - 5 Fill in blanks - 5 True/False - 1 Lab task - 1 Mini project - Summary & Homework Design: - Blue + Yellow premium coaching theme - Icons, flowcharts, comparison tables - Animation guidance (fade, bullet reveal) - Modern professional look This is PART 1. It will later be merged into final mega 400+ slide file. Generate now.
Detailed CBSE Class 11 Computer Science (083) Volume 1 Part 1 covering Chapters 1-8: Computational Thinking, Python Basics, Flow Control, Strings, Lists, Tuples, Dictionaries & Modules. Includes concepts, algorithms, flowcharts, Python programs, dry
Volume 1: Programming First Strategy PART 1
Chapters 1-8: Computational Thinking to Modules Strictly from Textbook - Detailed Concepts, Programs & Exercises
---
Photo by Pict4life on Unsplash

---
Photo by Eugenia Romanova on Unsplash

1
Problem-Solving Using Algorithms and Computational Steps
---
Photo by Ecliptic Graphic on Unsplash

> Computational thinking refers to the thought processes involved in formulating problems so their solutions can be represented as computational steps and algorithms. In education, computational thinking is a set of problem-solving methods that involve expressing problems and their solutions in ways that a computer could also execute.
— Wikipedia: Computational Thinking


---
Photo by razi pouri on Unsplash
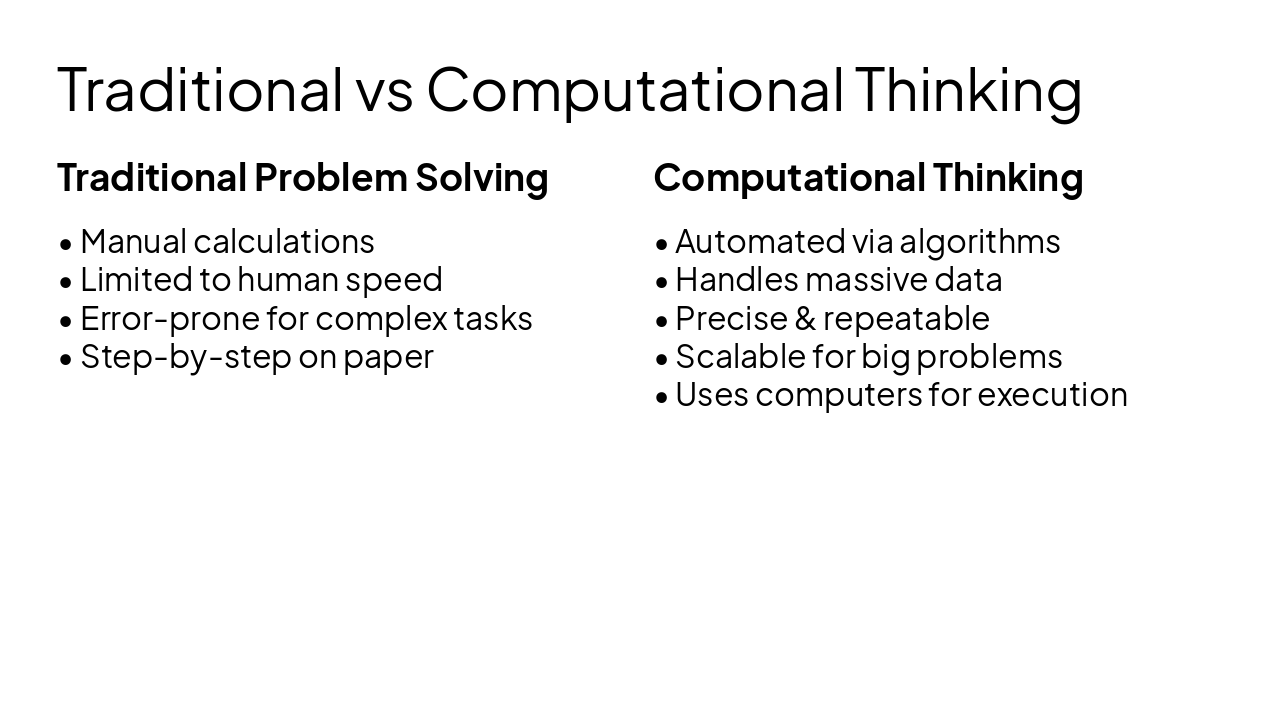
Traditional Problem Solving
Computational Thinking
> The maths taught around the world today does not fit how it is used in the real world. Computation technology is more accessible than ever before, but no curriculum in the world assumes it exists. Instead, it is focussed on the mechanics of hand calculation, rather than the essence of real-world maths.
— Conrad Wolfram (Advocate of Computational Literacy)
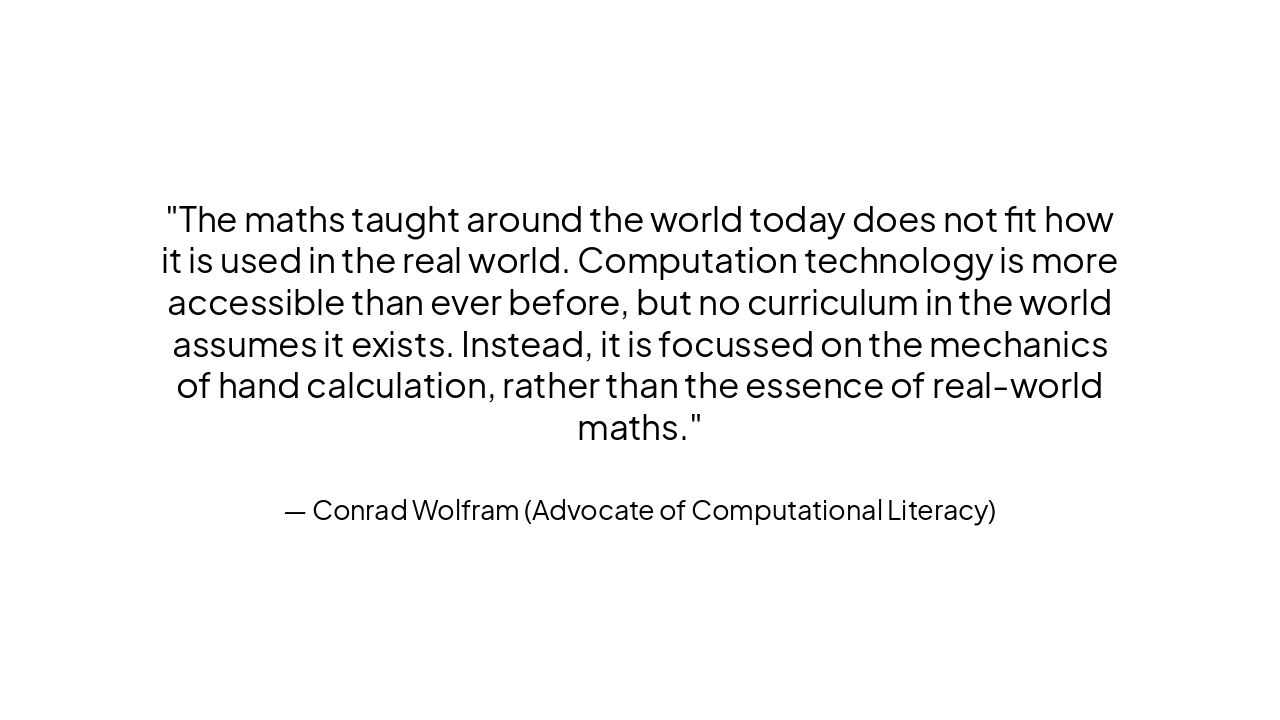

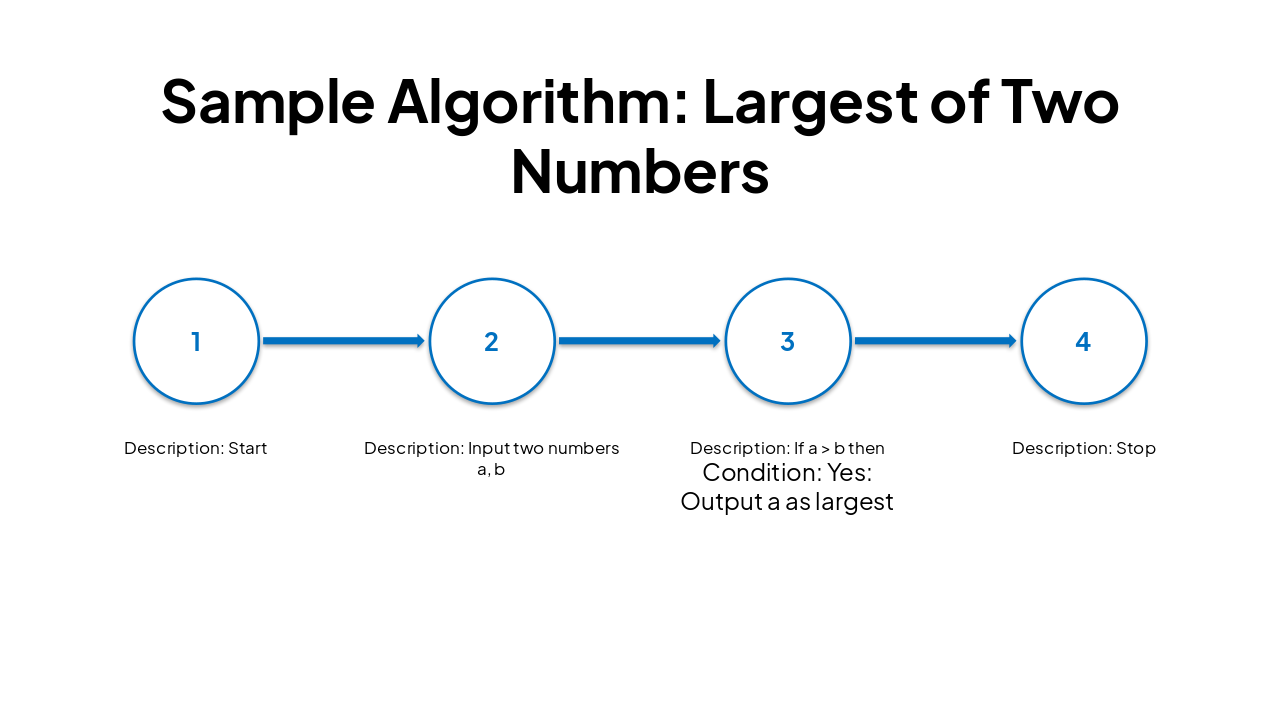
| Step No. | Description | Condition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Start | ||
| 2 | Input two numbers a, b | ||
| 3 | If a > b then | Yes: Output a as largest | No: Output b as largest |
| 4 | Stop |
---
Photo by Kelly Sikkema on Unsplash
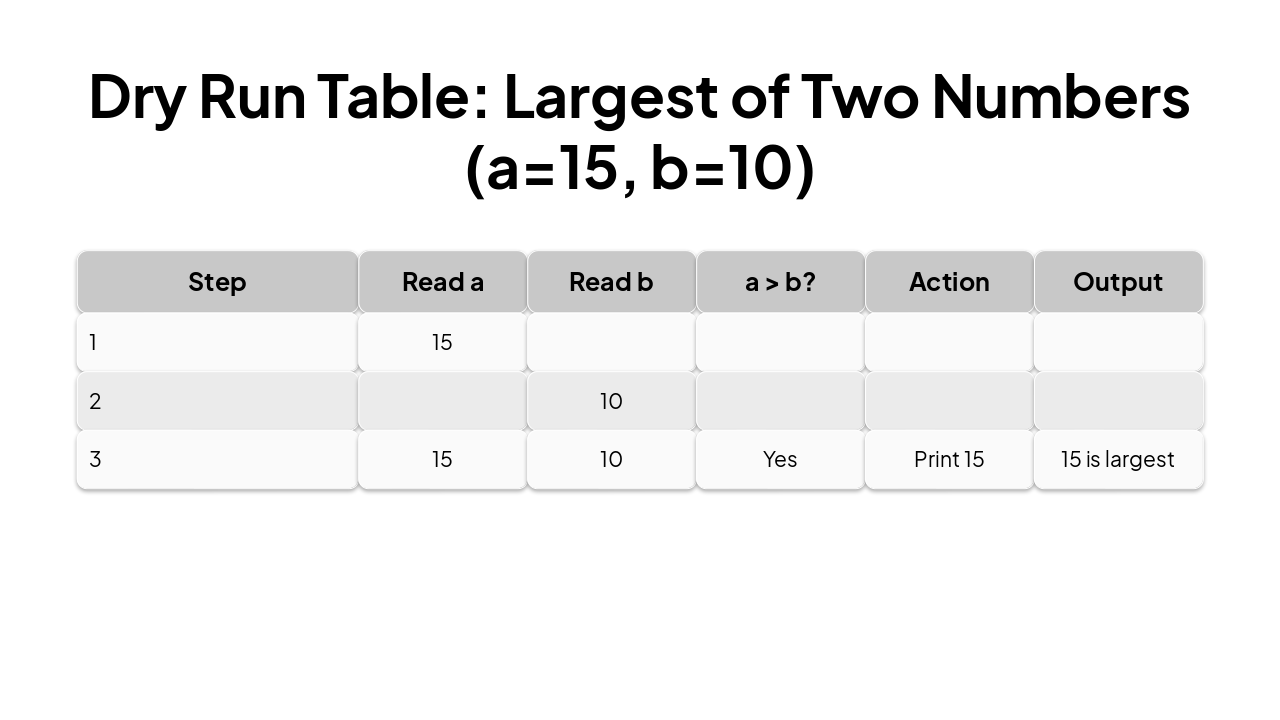
| Step | Read a | Read b | a > b? | Action | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | ||||
| 2 | 10 | ||||
| 3 | 15 | 10 | Yes | Print 15 | 15 is largest |
a = int(input("Enter first number: "))b = int(input("Enter second number: "))if a > b: print(a, "is larger")else: print(b, "is larger")Enter first: 20 Enter second: 15








Explore thousands of AI-generated presentations for inspiration
Generate professional presentations in seconds with Karaf's AI. Customize this presentation or start from scratch.